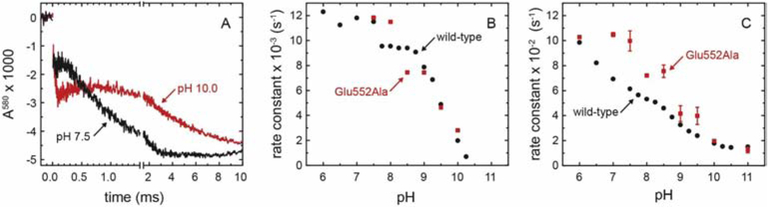
Figure 4. Electron-transfer kinetics.
The reduced CytcO was incubated under an atmosphere of CO and mixed in a stopped-flow apparatus with an O2-saturated solution. (A) Absorbance changes at 580 nm. The reaction was initiated at t = 0 by photolysis of the CytcO-CO complex (unresolved decrease in absorbance). The following small decrease in absorbance is associated with formation of the PR state. The increase in absorbance with a time constant of ~100 μs or ~400 μs at pH 7.5 and pH 10, respectively, is associated with the PR → F reaction. The final decrease in absorbance with time constants of 1 ms and 5 ms, respectively, is associated with formation of the oxidized (O) CytcO. The traces are scaled to 1 μM reacting enzyme. A laser artifact at t = 0 has been truncated for clarity. (B,C) pH dependence of the PR → F (B) and F → O (C) rate constants (red) compared to the equivalent rates obtained with the wild-type CytcO (black trace, [23, 43]).
The rates in (B) were obtained from measurements at 580 nm while those in (C) were obtained from measurements at 445 nm, 580 nm and 605 nm. The error bars are SD based on 2-4 measurements. Experimental conditions: the mixing ratio was 1:5. Syringe 1 contained 5 μM CytcO, 5 mM Bis-trispropane pH 8.0, 100 μM EDTA, 0.05 % DDM. Syringe 2 contained 33 mM of Bis-tris-propane, CAPS, and CHES supplemented with 100 μM EDTA, 0.05 % DDM.