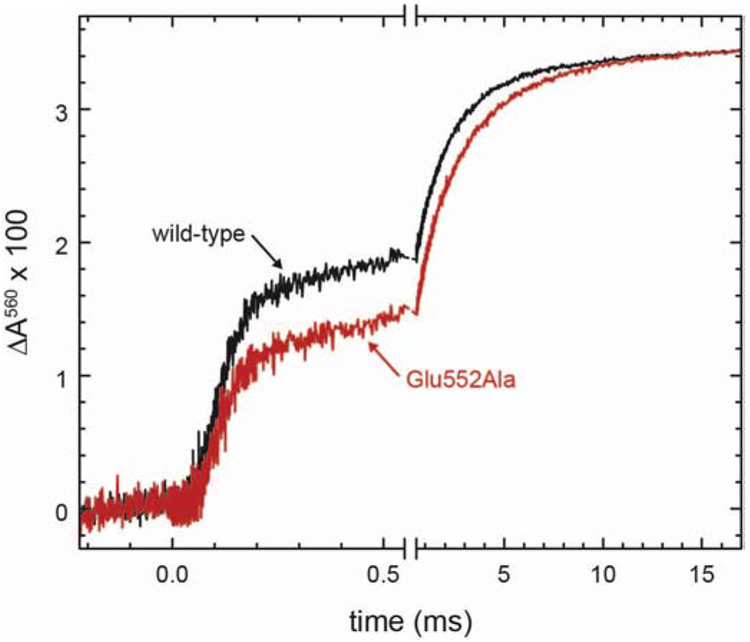
Figure 5. Proton-uptake kinetics.
The reduced CytcO was incubated under an atmosphere of CO in a solution containing the pH dye phenol red, in the absence of buffer. The experiment was carried out as described in Figure 4. An increase in absorbance is associated with proton uptake. For comparison of the relative amplitudes of the two kinetic components, the Glu552Ala (red) and wild-type (black) traces have been scaled to yield the same total amplitude. To remove absorbance changes that are not associated with changes in protonation, the experiments were repeated with buffer at pH 7.8 (syringe 2 contained 100 mM HEPES pH 7.8 instead of KCl) and the absorbance changes were subtracted from those obtained in the absence of buffer. Experimental conditions before mixing (1:1): syringe 1 contained: 100 mM KCl (pH 7.8), 100 μM EDTA, 40 μM phenol red, 0.05 % DDM; 2 mM ascorbate; 0.2 μM hexaammineruthenium(11) chloride (HexaRu(11)), 10-20 μM CytcO. Syringe 2 contained an oxygen-saturated solution (~1.2 mM) with the same composition as that in syringe 1, except that no ascorbate/HexaRu(11) were added.