Figure 1.
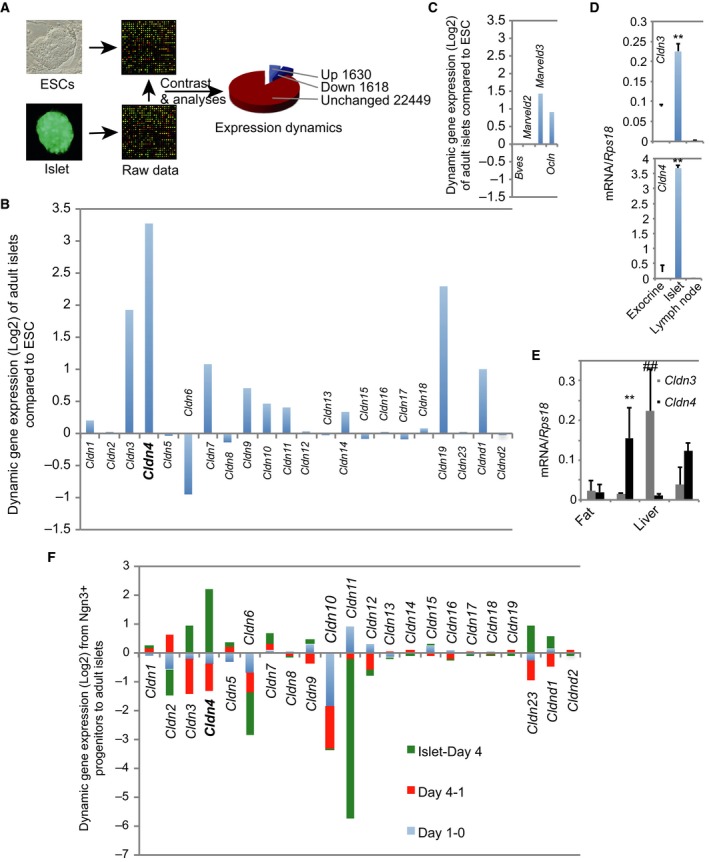
Claudin 4 is highly expressed in adult functional islet cells. (A) Scheme depicted of the process of analysing transcriptomic data sets. Analyses of transcriptomic data sets generated from RNA extracted from ESCs and isolated adult islets. (B) Bioinformatics contrast analyses of the TJ claudin (Cldn) family genes with Cldn4 bolded and enlarged. (C) Differential contrast analyses of the TJ‐associated genes of occludin family. (D) qRT‐PCR analysis of adult islet Cldn3 and Cldn4. RNA was extracted from the pancreatic exocrine tissue (a epithelial tissue), the isolated adult islets and lymph nodes (a mesenchymal tissue). Data presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, **P < 0.01 compared to exocrine or lymph node (Mann–Whitney U tests). (E) qRT‐PCR analysis of Cldn3 and Cldn4 in selected metabolic tissues. RNA was extracted from fat, renal tissue, the liver and skeletal muscle. Data presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, **P < 0.01 compared to fat or the liver; ## P < 0.01 compared to all other tissues (Mann–Whitney U tests). (F) Claudin 4 (bolded and enlarged) is predominantly up‐regulated during functional maturation of islet β cells. Bioinformatics analyses of the claudin (Cldn) family genes in global gene expression data sets 25 during in vitro differentiation of islet progenitors for 0 (Day 0, namely undifferentiated islet progenitors)‐, 1 (Day 1, namely 1‐day differentiation of islet progenitors)‐ and 4 (Day 4, namely 4‐day differentiation of islet progenitors)‐day differentiation and using adult islets (islet) as the reference.
