Figure 1.
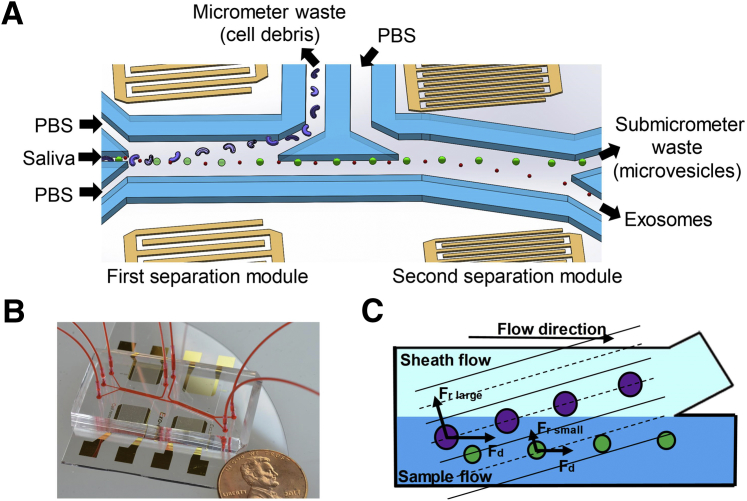
Schematics and mechanism of the device. A: Schematic of the acoustofluidic device for salivary exosome separation. The device has two modules using 20-MHz and 40-MHz surface acoustic waves (SAWs) for micrometer and submicrometer particle separation. B: An optical image of the integrated acoustofluidic device (penny shown for size comparison). C: Size-based separation occurs in each module. Due to the acoustic radiation force (Fr) induced by a SAW field and a drag force induced by fluid (Fd) large particles are separated into a sheath flow, whereas smaller particles remain in the primary sample flow. PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.