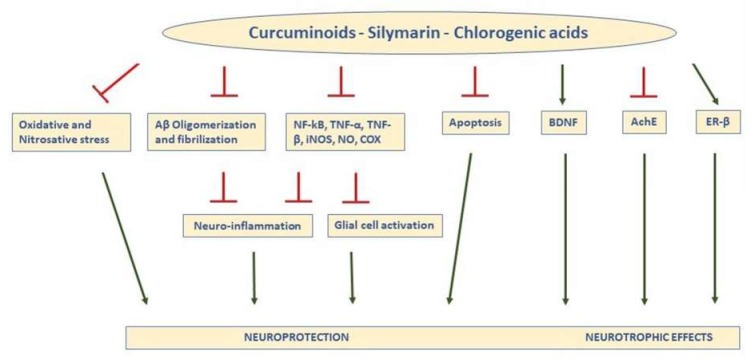
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the main actions responsible for the neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of curcuminoids, silymarin, and Chlorogenic acids (CGA) in the brain. In general, the compounds inhibit oxidative and nitrosative stress, prevent formation of Aβ aggregates and fibrils, and reduce expression and activity of inflammatory agents, leading to less neuroinflammation and glial activation, decreasing apoptosis, increasing BDNF, inhibiting AChE, and binding ER-β, (T indicates inhibitory effects). TNF-a: tumor necrosis factor-a; NFkB: nuclear factor kappa light-chain enhancer of activated B cells; TNF-β, tumor necrosis factor-β; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; NO: nitric oxide; COX: cyclooxygenase; ER-β: estrogen receptor-β; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; AChE: acetylcholinesterase.