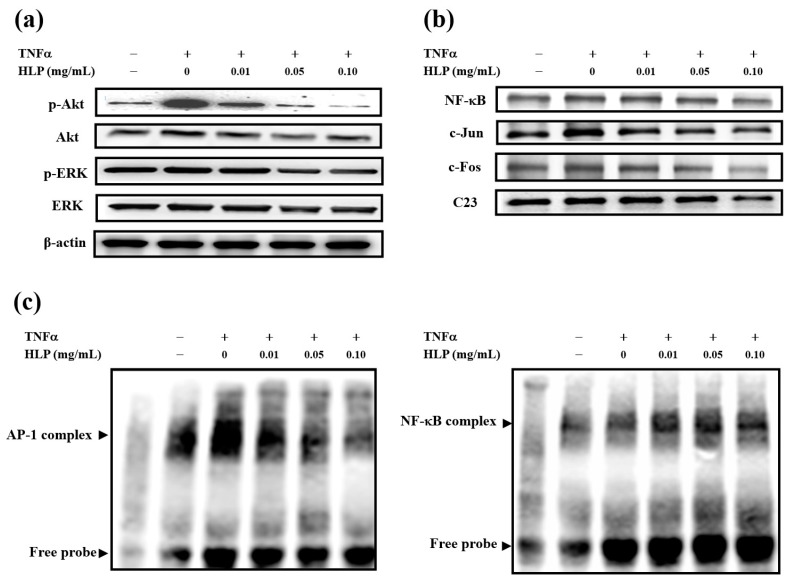
Figure 3.
Effect of HLP on TNF-α-induced Akt/AP-1 signaling in VSMCs. A7r5 cells were treated with TNF-α (10 ng/mL) in the absence or presence of various concentrations (0, 0.01, 0.05 and 0.10 mg/mL) of HLP for 24 h; (a) the cytoplasmic fraction was analyzed for the expressions of p-Akt, Akt (protein kinase PKB, also known as Akt), p-ERK, and ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase), and (b) the nuclear fraction was analyzed for the expressions of NF-κB, c-Jun, and c-Fos, two components of activator protein-1 (AP-1). These protein levels were determined by Western blotting. β-actin and C23 served as a cytoplasmic and nuclear internal control, respectively. (c) The nuclear extracts were analyzed for AP-1 (left panel) and NF-κB (right panel) DNA-binding activities using biotin-labeled AP-1 and NF-κB specific oligonucleotide by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). Lane 1 represents nuclear extracts incubated with unlabeled oligonucleotide (free probe) to confirm the specificity of binding. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. +, added; −, non-added.