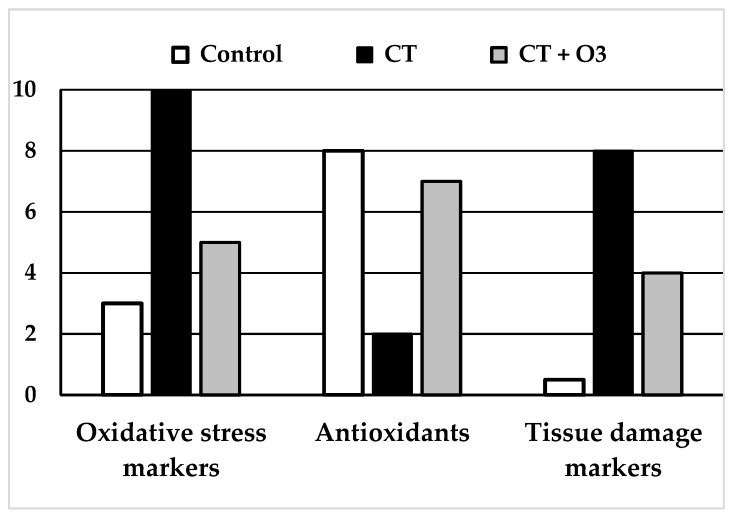
Figure 2.
Schemes of results obtained in the experimental studies using systemic ozone therapy (rectal or intraperitoneal) using chemotherapy drugs. (Left and Middle): “Oxidative stress markers” (MDA: malondialdehyde, TBARS: thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances) and “Tissue damage markers” (creatinine, pro-BNP: pro-brain natriuretic peptide) increased largely and significantly with chemotherapy. The increase was significantly lower in rats with chemotherapy + ozone therapy. (Middle): levels of “Antioxidants” (GSH: glutathione, SOD: superoxide dismutase, CAT: catalase and GSH-GPx: glutathione peroxidase) decreased in chemotherapy group whereas those contents were closer to the control group in rats treated with chemotherapy + ozone therapy. All differences were statistically significant.