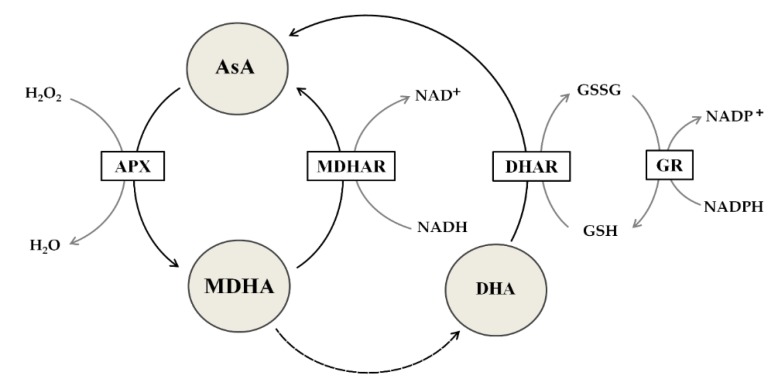
Figure 2.
The ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Detoxification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) occurs due to the action of ascorbate peroxidase (APX). APX uses ascorbic acid (AsA) as an electron donor to produce monodehydroascorbate (MDHA), which is then reduced to AsA by monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR), whose cofactor is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Dehydroascorbate (DHA), which is formed by disproportionation, is reduced to AsA by the action of dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), the cofactor of which is reduced glutathione (GSH). As a result of DHAR’s activity, GSH is oxidized to glutathione disulfide (GSSG), which is then reduced to GSH as a result of the activity of glutathione reductase (GR), which acquires electrons from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH).