FIGURE 1.
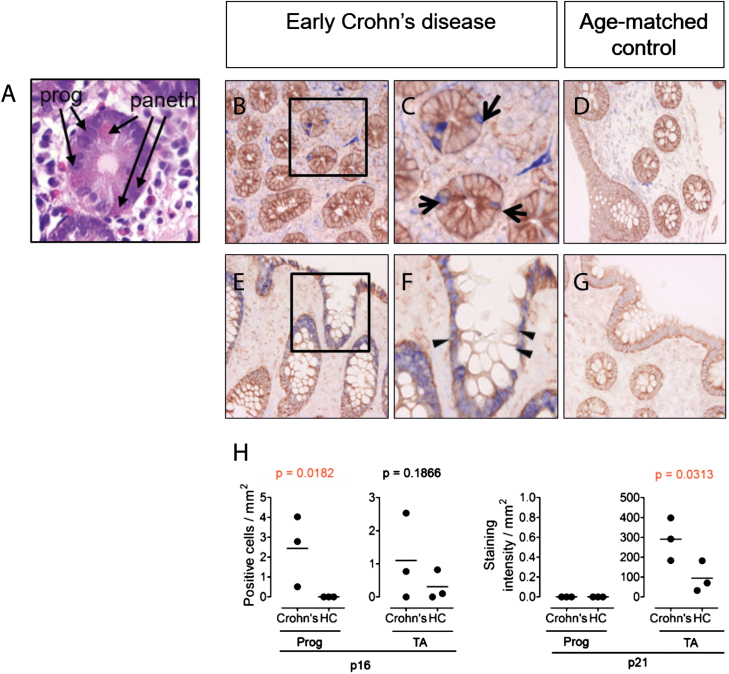
The stem and transient amplifying cell niches of the intestine contain potentially senescent cells in Crohn’s disease. In all immunostains, epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR, brown) is used as a counterstain to provide tissue architecture. (A) H&E staining of intestinal tissue showing characteristic eosin rich cytoplasmic staining (pink) morphology of paneth cells, confirming localization at level of progenitor cell niche. (B-G) Immunostaining for p16 and p21 (blue) of intestinal tissue from a patient with early Crohn’s disease (B,C,E,F) and age/sex-matched control (D,G). (H) Quantification of p16 and p21 positive cells in progenitor (Prog) and transient amplifying (TA) cell niches in intestinal tissue from early Crohn’s patients (n = 3), compared to age-matched healthy controls (HC). One-tailed Mann Whitney U testing was used for statistical analysis. Exact P-values are given. p16+ or p21+ cells in the progenitor cell niche in the gut were identified based on localization in close proximity to the paneth cells. Methods: Antigen retrieval was performed for 20 minutes with a solution of 1 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) on paraffin sections. Mouse anti-human p16 (Roche clone E6H4, ready to use; blue), mouse anti human p21 (DAKO, clone SX118, 1:20; blue) and rabbit anti-human epithelial growth factor receptor (Abcam clone EP38Y, 1:500; brown) were used with the Lab Vision MultiVision Polymer Detection System anti Mouse-AP anti-rabbit-HRP staining kit (Thermofisher) to detect p16+ and p21+ cells. Arrows denote the progenitor cell niche in the intestine. Triangles denote the transient amplifying cell niche. Intensity of p21 immunostaining in intestine was quantified as pixel intensity.