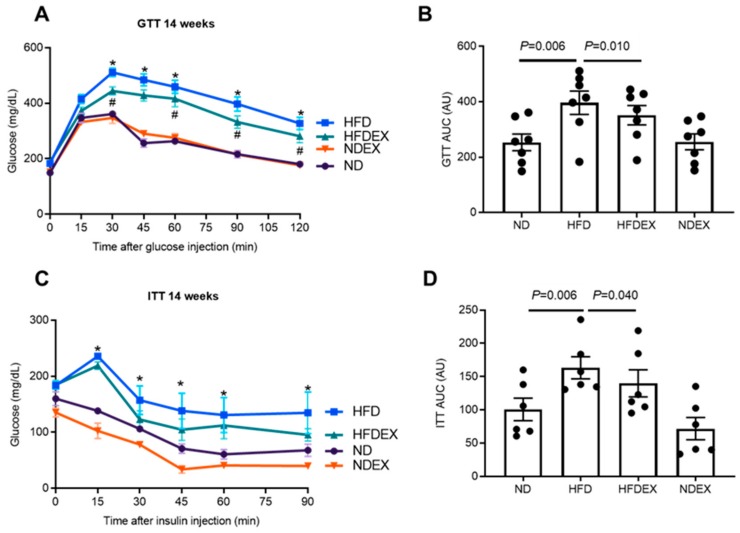
Figure 2.
Exercise training prevents HFD-induced development of T2DM phenotype. (A) and (B) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (GTT) at 14-week treatment in the four groups of mice: normal diet (ND), high-fat diet (HFD), HFD mice on exercise training (HFDEX), and ND mice on exercise training (NDEX). Blood glucose was measured for 2 h at several time points after the injection of glucose. Glucose clearance was decreased in HFD but improved with EX. N = 8. (C) and (D) Intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test (ITT) at 14-week treatment. Blood glucose concentrations were measured for 1.5 h after the injection of insulin. Insulin resistance was higher in HFD as compared to the ND group. * P < 0.05 between ND and HFD. # p < 0.05 between HFDEX and HFD. All values are expressed as mean ± SEM with dots representing each animal. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc test were used for statistical analysis.