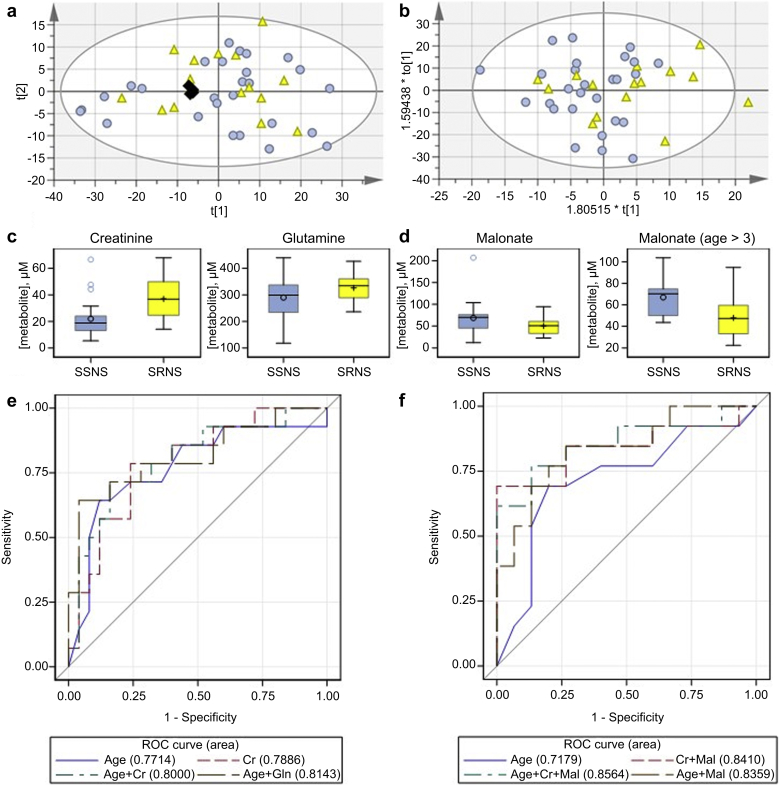
Figure 2.
Metabolite biomarkers to predict steroid resistance. Score plots for binned data comparing steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS) (n = 27) and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) (n = 15) pretreatment samples: (a) Principal component analysis, R2X(cum) 0.904; Q2(cum) 0.803. (b) Orthogonal partial least-squares discriminate analysis scores plot R2X(cum) 0.719; R2Y(cum) 0.16; Q2(cum) −0.0467; SSNS Pre, light blue circle; SRNS Pre, yellow triangle; pools, black diamond. (c) Box plots showing the pretreatment concentration by phenotype of metabolites selected by stepwise selection algorithms for inclusion in a logistic regression model of the odds of SRNS among subjects of all ages. (d) Box plots showing the pretreatment concentration by phenotype of malonate, which was significantly different between patients >3 years of age with SSNS versus SRNS. (e) A logistic regression model comparing the known risk factor age with metabolites for prediction of SRNS. (f) A logistic regression model comparing the known risk factor, age, with metabolites for prediction of SRNS in patients >3 years of age. ROC, receiver operating characteristic.