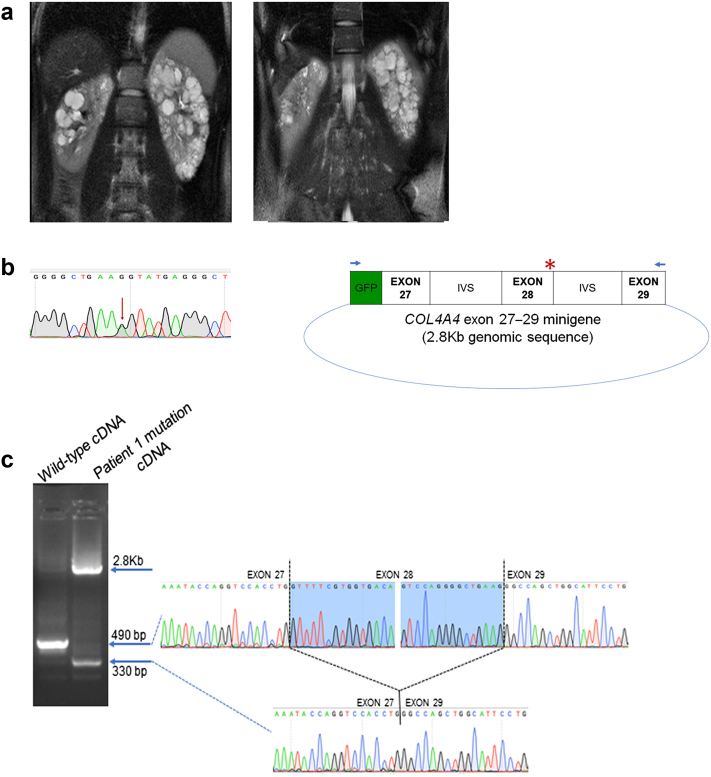
Figure 1.
(a) Magnetic resonance image of the abdomen from patient 1 showing both kidneys with several small to moderate cysts. Imaging at enrollment into the CRISP study (left image) and at 4-year follow-up into the CRISP study (right image) is shown. (b) (Left) Sanger sequence tracing showing the heterozygous substitution variant (red arrow) COL4A4: exon28: c. G2383A in patient 1. (Right) Minigene plasmid containing green fluroescent protein (GFP) contiguous with the 2.8-Kb COL4A4 genomic sequence that includes exons 27–29 and the intervening intronic sequences (IVSs). The red asterisk denotes the position of the COL4A4 variant in patient 1. Blue arrows indicate the primer locations used for reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction that selectively amplify the minigene sequence and avoid amplification of the native COL4A4 transcript. (c) (Left) Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction products from the wild-type splice form (490-base pair [bp]) and from the mutation (2.8-Kb unspliced product and 330-bp product resulting from complete skipping of exon 28). (Right) Sanger sequencing of the wild-type and 330-bp mutated cDNA showing that exon 27 is spliced directly to exon 29 as result of the mutation.