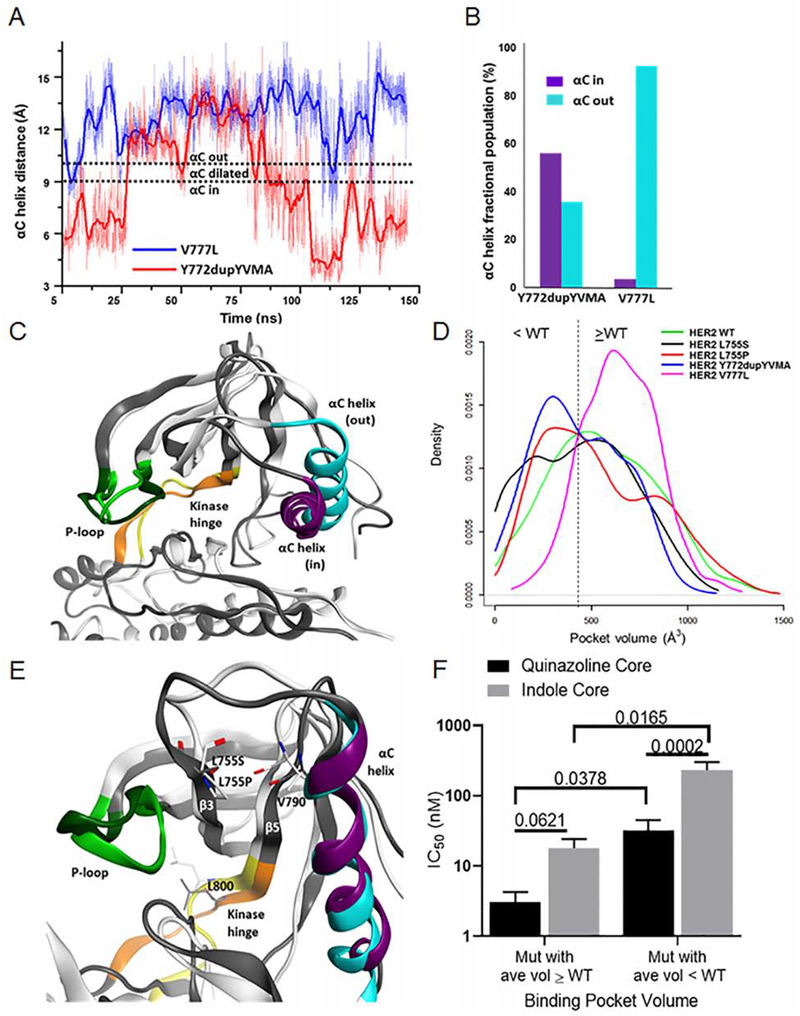
Figure 5:
MDS of HER2 mutants reveal possible mechanisms for decreased drug sensitivity for Y772dupYVMA and L755P mutations. (A) αC-helix positions for the HER2 V777L and Y772dupYVMA exon 20 mutants during the 150 ns accelerated MDS. (B) Fractional population of molecular dynamics snapshots for the HER2 exon 20 mutants in the αC-helix “in” vs. “out” conformations. (C) Molecular dynamics snapshots of the V777L (white backbone, light green P-loop) and Y772dupYVMA (grey backbone, dark green P-loop) mutants. Note minor differences in P-loop and kinase hinge conformations but a significant shift in αC-helix position (“out” position for V777L in blue, “in” position for Y772dupYVMA in purple). (D) Binding pocket volume profiles for the HER2 mutants taken from the accelerated MDS. (E) Molecular dynamics snapshots of L755P (white, backbone; light green, P-loop; yellow, hinge; blue, αC-helix) and L755S (grey, backbone; dark green, P-loop; orange, hinge; purple, αC-helix) HER2 mutants. (F) Bar plots of IC50 values of HER2 mutants with binding pocket volumes ≥ WT HER2 or smaller than WT HER2 treated with quinazoline or indole based TKIs. Bars are representative of mean ± SEM (n ≥ 3). See also Figure S4.