Figure 7.
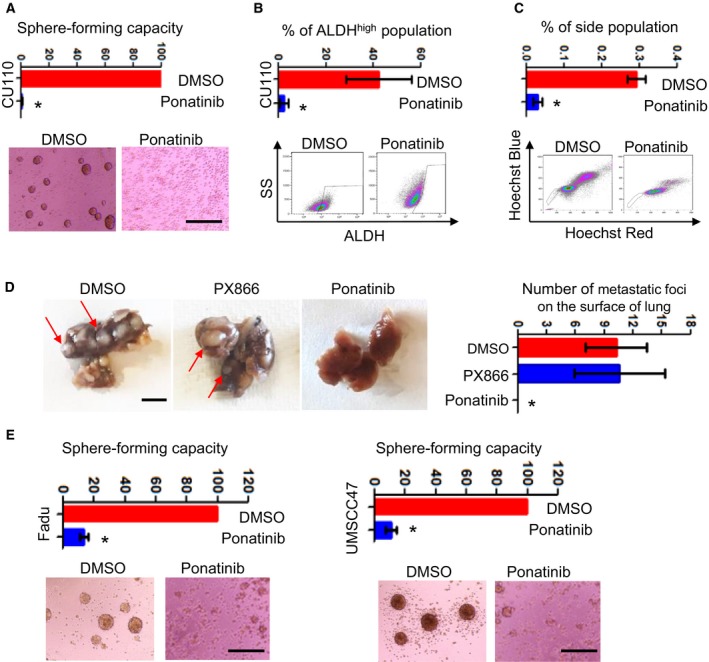
Ponatinib, a multi‐kinase inhibitor targeting Ephs, TRKs and c‐Kit, effectively eliminates CSC population in HNSCC. (A) HNSCC Sphe‐forming assay of CU110 cells treated with ponatinib. The quantification is shown on top. Sphes with diameter ≥ 30 μm were counted. n = 3; error bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05 (two‐tailed Student t‐test). Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) FACS analysis of ALDH in CU110 cells treated with ponatinib. The quantification is shown on top. n = 3; error bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05 (two‐tailed Student t‐test). (C) FACS analysis of SP fraction in CU110 treated with ponatinib (left). The quantification is shown on top. n = 3; error bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05 (two‐tailed Student t‐test). (D) Left: Gross pictures of lung tissues harvested from mice received tail vein injection of CU110 cells treated with DMSO, PX866 or ponatinib. Red arrow indicates metastatic foci on the surface of the lung. Right: Relevant quantification of the metastatic foci on the surface of lung. n = 4; error bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05 (two‐tailed Student t‐test). Scale bar: 100 µm. (E) Effect of ponatinib on reducing CSC population in human HNSCC cell lines: Fadu and UMSCC47, using Sphe‐forming assay. The quantification is shown on the right. n = 3; error bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05 (two‐tailed Student t‐test). Scale bar: 100 µm.
