Figure 2.
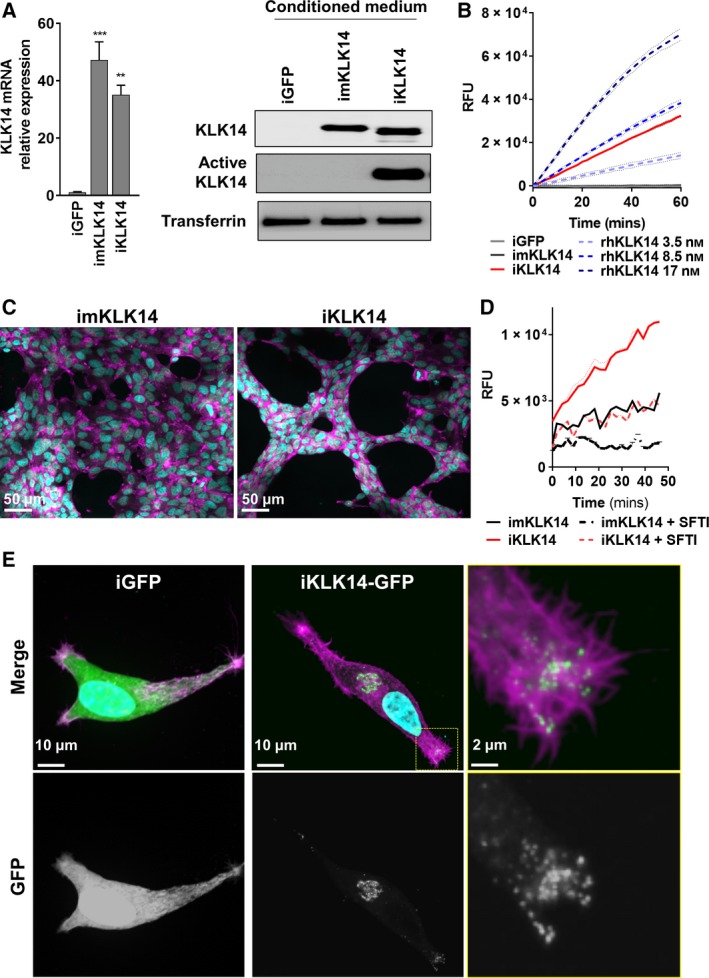
KLK14 proteolytic activity alters the morphology of LNCaP cells. (A) Left: KLK14 mRNA level determined by RTqPCR in LNCaP iGFP, imKLK14, and iKLK14 cells after 72 h of doxycycline treatment (mean ± SD). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to iGFP cells, two‐way ANOVA test. Right: Expression of KLK14 protein determined by western blot on concentrated CM. (B) KLK14 proteolytic activity in concentrated CM from iGFP‐, imKLK14‐, and iKLK14‐LNCaP cells compared to activity of active rhKLK14 (3.5, 8.5, and 17 nm) using a specific KLK14‐FRET peptide (mean ± SD). (C) Fluorescence microscopy imaging of imKLK14‐ and iKLK14‐LNCaP cells grown 3 days in serum‐free condition containing doxycycline and stained for F‐actin (phalloidin, purple) and nucleus (DAPI, blue). Scale bar: 50 µm. (D) KLK14 proteolytic activity in concentrated CM from imKLK14 and iKLK14‐LNCaP cells grown in serum‐free condition containing doxycycline ± selective KLK14 inhibitor (SFTI‐WCIR 2.5 µm) for 3 days (mean ± SD). (E) Fluorescence microscopy imaging of KLK14‐GFP and GFP in iKLK14‐GFP and iGFP ‐LNCaP cells costained for F‐actin (phalloidin, purple) and nucleus (DAPI, blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. GFP: green fluorescent protein; rhKLK14: Recombinant human KLK14; SFTI: sunflower trypsin inhibitor.
