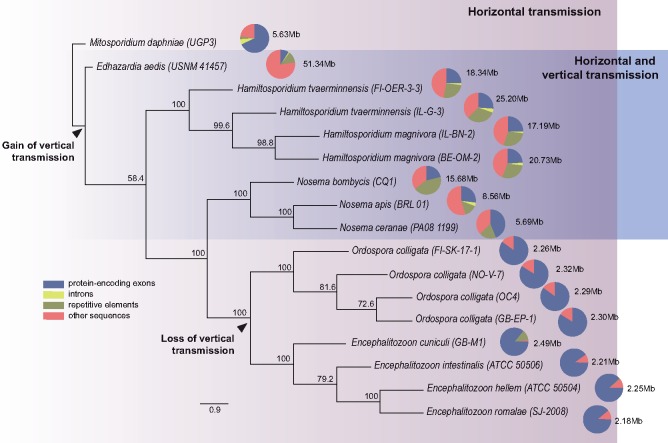
Fig. 1.
—Phylogenetic reconstruction of the history of 12 microsporidia with well-known transmission modes, based on 27 orthologous protein sequences. Mitosporidium daphniae, another horizontally transmitted gut parasite of Daphnia magna, is used as the root. Edhazardia aedis is a parasite of the mosquito Aedis aegypti transmitted vertically from adult hosts to their larval progeny, and horizontally among larvae (Desjardins et al. 2015). Nosema bombycis, a microsporidian parasite of the silkworm, as well as Nosema ceranae and Nosema apis, which are found in the honey bee, are vertically and horizontally transmitted; N. bombycis is transmitted through the host eggs (Han and Watanabe 1988), N. ceranae and N. apis, are sexually transmitted through the sperm of drones (Roberts et al. 2015). Among the Encephalitozoon species, Encephalitozoon romalae is found specifically in grasshoppers, whereas the other three species infect a broad range of mammals including humans. Although transplacental transmission is reported for Encephalitozoon cuniculi, horizontal transmission is the predominant transmission route of parasites from this genus (Cali and Takvorian 2014). Proportions of sequences within assemblies are indicated by pie charts with assembly sizes indicated next to the pie charts.