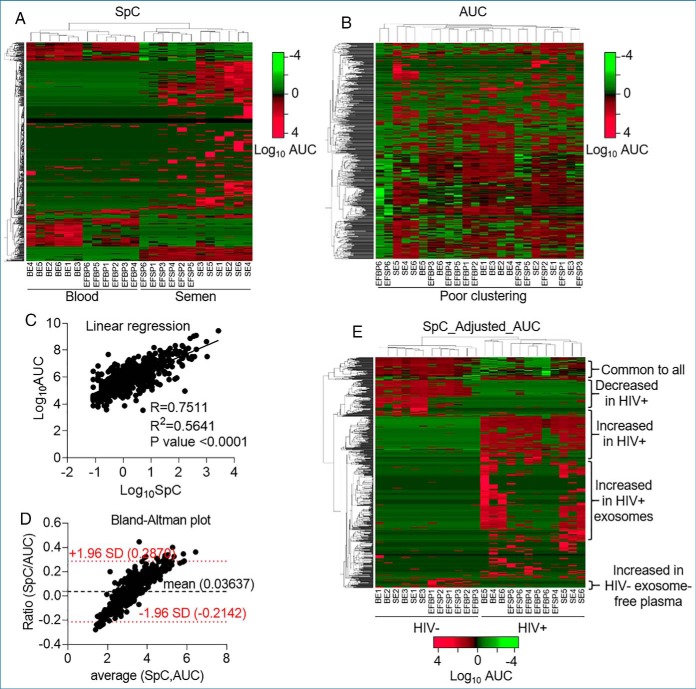
Fig. 3.
Sample clustering and data normalization. A, Double-clustering (Euclidean, average linkage) heatmap of SpC data showing efficient body-fluid (blood versus semen) based separation. B, Double-clustering (Euclidean, average linkage) heatmap depicting loosely clustered AUC data set without directionality. C, Linear regression showing correlation between SpC and AUC data sets for the mean of each of the 587 common proteins. Pearson R, R2 and p value are shown. D, Bland-Altman plot of the ratio SpC/AUC as a function of the average of the two methods showing the bias and agreement between the SpC and AUC data. The bias of 0.03637 unit is represented by the gap between the x axis, corresponding to zero differences, and the parallel line to the x axis at 0.03637 units. The red dotted lines are representations of the 95% limits of agreement, from −1.96 to +1.96. Hybrid data set showing integration of SpC and AUC data sets (SpC_Adjusted_AUC). Adjustments were made where peptides with detectable AUC, but undetectable spectral count were removed from the data set, resulting in a new list of 587 proteins. The analysis produced reliable visual representation of the data set revealing donor-, body-fluid, and HIV- dependent differences.