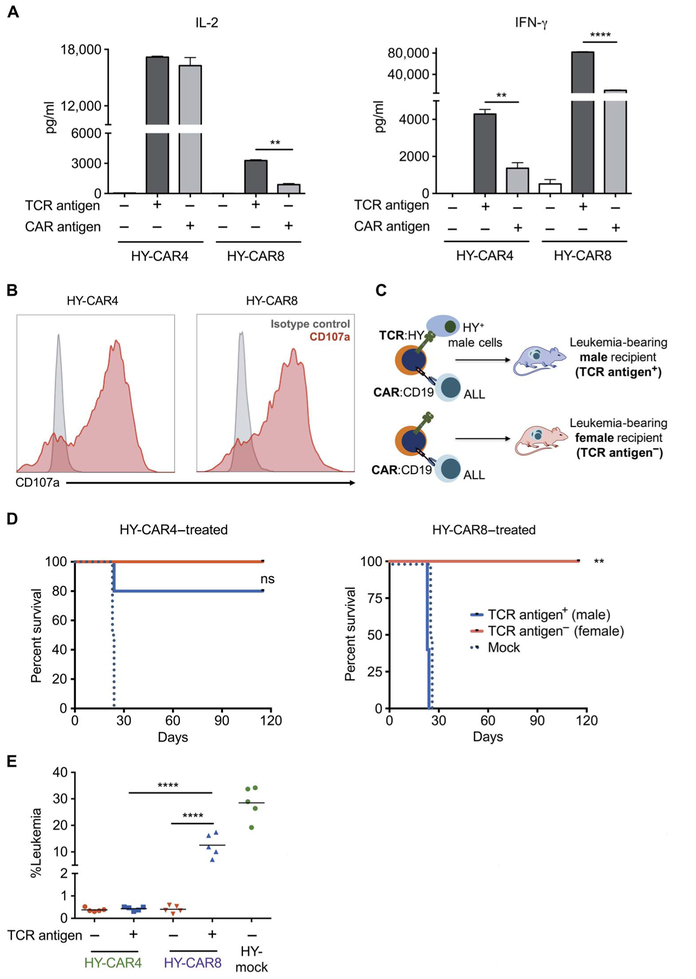
Fig. 2. Exposure of both TCR and CAR antigens diminishes efficacy of CAR8 but not CAR4 cells.
(A) IL-2 and IFN-γ production by HY-CAR4 and HY-CAR8cells after10hoursofincubationwithCD19KOfemalesplenocytes (CD19−/HY−), CD19KO male splenocytes (CD19−/HY+), or wild-type (WT) female splenocytes (CD19+/HY−) (**P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). (B) CD107a expression (red) and isotype control (gray) on HY-CAR T cells after 4 hours of incubation with CD19+ E2aPbx ALL. (C) HY-CAR4 or HY-CAR8 cells were administered on day 4 to E2aPbx-bearing syngeneic male (HY+) and female (HY−) recipients. (D) Survival of female (TCR antigen−) and male (TCR antigen+) recipients after treatment with 1 × 106 HY-specific CAR4 or CAR8 cells (n = 5 per group; **P < 0.01). (E) Leukemia burden in the bone marrow 7 days after infusion of mice treated with HY-CAR4 or HY-CAR8 cells (****P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA performed for all comparisons and log-rank Mantel-Cox test for survival analysis).