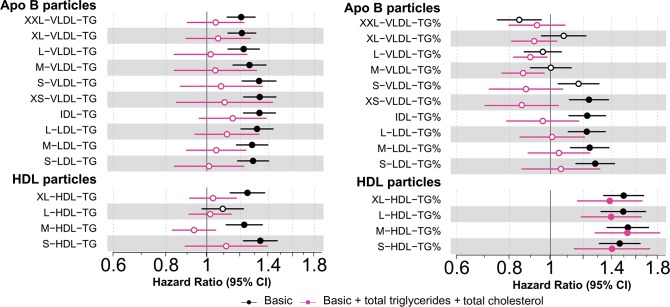
Fig 5. Observational associations of circulating triglyceride concentrations and triglyceride composition in lipoprotein subclass particles and risk of incident CHD.
(Left panel) Black: Hazard ratios for incident CHD per SD higher triglyceride concentration within each size-specific lipoprotein subclass adjusted for traditional risk factors. Pink: adjusted for traditional risk factors, serum cholesterol, and serum triglycerides. (Right panel) Black: Hazard ratios for incident CHD per SD higher percentage of triglycerides (of all lipid molecules) within each size-specific lipoprotein subclass adjusted for traditional risk factors. Pink: adjusted for traditional risk factors, serum cholesterol, and serum triglycerides. Basic risk factors include age, sex, mean arterial pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lipid medication, geographical region in FINRISK, and ethnicity in SABRE. The horizontal bars to the 95% CIs. Closed circles represent statistical significance of associations at P < 0.002 and open circles associations that are nonsignificant at this threshold. The horizontal bars refer to the 95% CIs. Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. Apo B, apolipoprotein B; CHD, coronary heart disease; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein; TG, triglycerides.