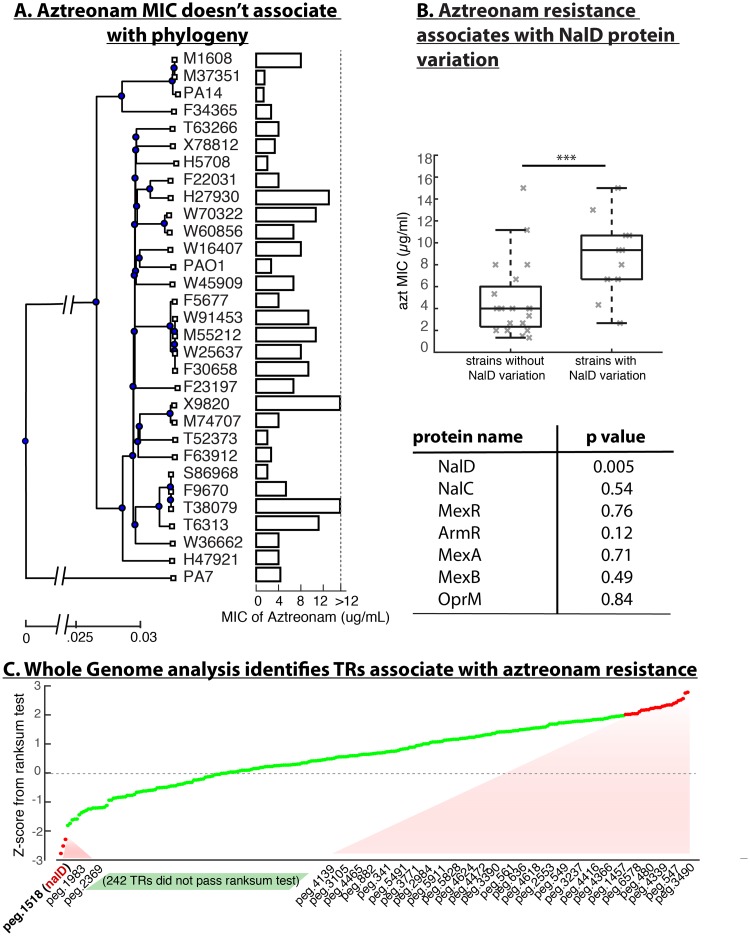
Fig 1. Aztreonam resistance is associated with variation in NalD across independent clinical isolates from acute P. aeruginosa infection.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of isolates from acute infections of cancer patients reconstructed from core genes, including the type strains PA14, PAO1 and PA7. The minimal inhibitory concertation (MIC) of the aztreonam varies significantly across the phylogenetic tree, showing it is not a phylogenetically conserved trait. (B) NalD protein is the only protein in the mexAB-oprM efflux pathway that is strongly associated with aztreonam MIC in a rank sum test (***, p = 0.005). The table on the bottom shows the p-values for rank sum tests conducted on other proteins known from the mexAB-oprM efflux system and its regulatory pathway. (C) Expanding the analysis to all the transcriptional regulators encoded by the P. aeruginosa genome revealed 30 candidates whose protein sequences variation were associated with aztreonam MIC (see S2 Table), but NalD remained the strongest correlate.