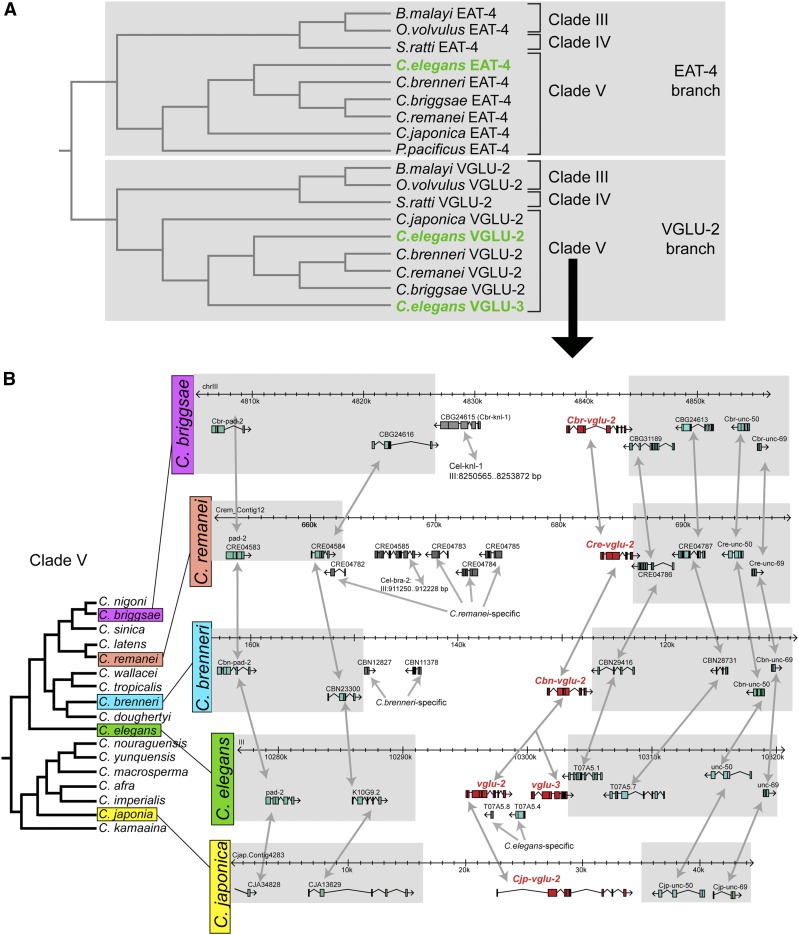
Figure 3.
Analysis of VGLUT sequences from different nematode species indicates a C. elegans-specific VGLUT duplication. (A) VGLUT homologs in a broad sampling of different nematode species. Clades are according to Blaxter et al. (1998). Identifiers are Strongyloides ratti genes: EAT-4 = SRP11984; VGLU-2 = SRP11109; for Onchocerca volvulus VGLU-2 = OVP03707, and Brugia malayi = BM46758. (B) vglu-2 duplication occurred specifically in C. elegans, but not in other Elegans supergroup species. Syntenic genomic intervals from several representative Caenorhabditis species from the Elegans supergroup. Gray shading and double-headed arrows indicate synteny. The phylogenetic tree is redrawn from Félix et al. (2014). The T07A5.4 gene (erroneously called ostf-4 in WormBase) that is located between vglu-2 and vglu-3 is a C. elegans-specific duplicate of the highly conserved F37C4.5 gene located on a different chromosome.