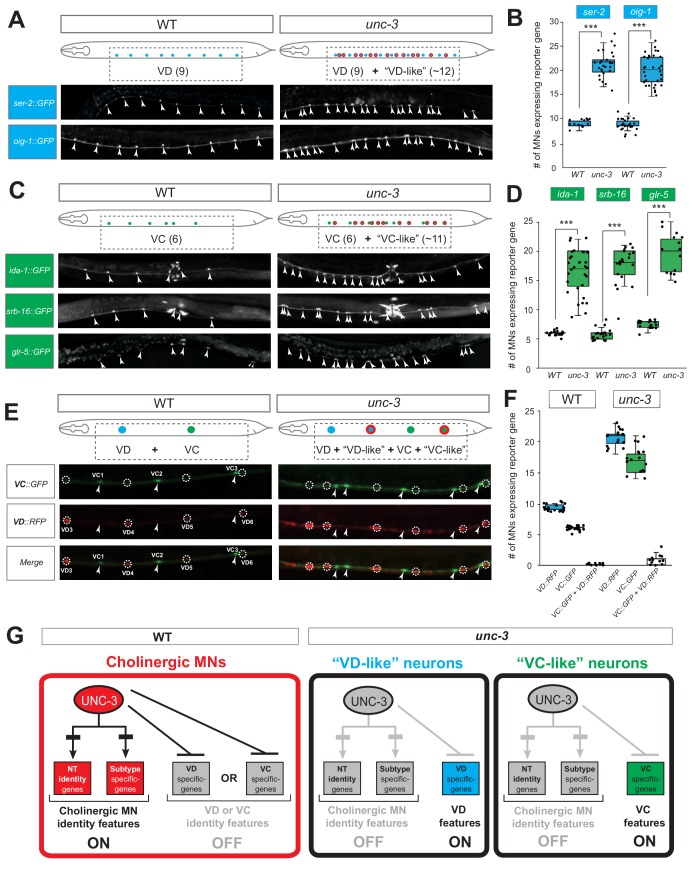
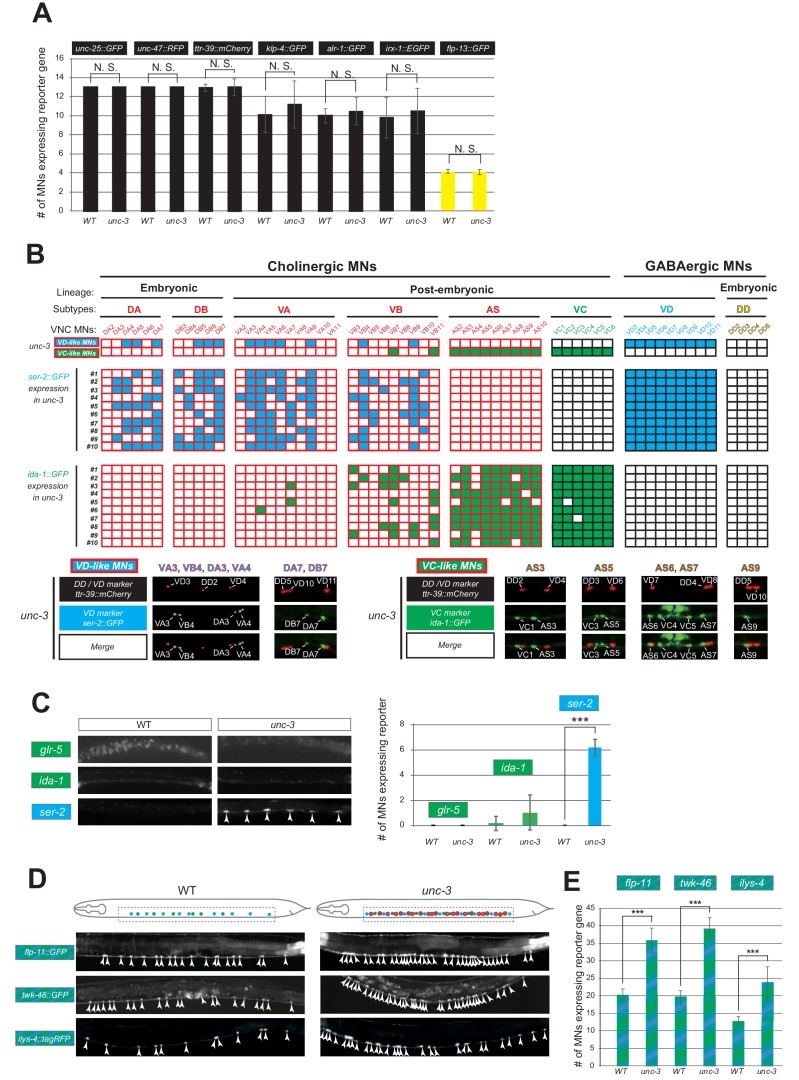
Figure 2. UNC-3 has a dual role in cholinergic ventral cord motor neurons.
(A) Terminal identity markers of VD neurons (ser-2, oig-1) are ectopically expressed in unc-3-depleted MNs. Representative images of larval stage 4 (L4) hermaphrodites are shown. Similar results were obtained in adult animals. Arrowheads point to MN cell bodies with gfp marker expression. Green fluorescence signal is shown in white for better contrast. Dotted black box indicates imaged area. (B) Quantification of VD markers (ser-2, oig-1) in WT and unc-3 (n3435) at L4. N > 15. ***p<0.001. For details on box plots, see Materials and methods. (C) Terminal identity markers of VC neurons (ida-1, srb-16, glr-5) are ectopically expressed in unc-3-depleted MNs. Representative images of larval stage 4 (L4) hermaphrodites are shown. Similar results were obtained in adult animals. Arrowheads point to MN cell bodies with gfp marker expression. Green fluorescence signal is shown in white for better contrast. Dotted black box indicates imaged area. (D): Quantification of VC markers (ida-1, srb-16, glr-5) in WT and unc-3 (n3435) at L4. Individual data points are dot-plotted. N > 15. ***p<0.001. (E) Distinct MNs acquire VC-like or VD-like terminal identity features in unc-3 (n3435) mutants. The VC marker in green (ida-1::gfp) and the VD marker in red (ser-2::rfp) do not co-localize in WT or unc-3 (n3435) mutants. Representative images are shown. Individual VC/VC-like and VD/VD-like neurons are pointed and circled, respectively,(VD: dotted circles; VC: arrowheads) to highlight that an individual MN never expresses both markers. (F) Quantification of data shown in E. N > 16. (G) Schematic that summarizes the dual role of unc-3. Apart from activating cholinergic MN terminal identity genes, UNC-3 prevents expression of VD and VC terminal features in distinct cells (‘VD-like’ versus ‘VC-like’).