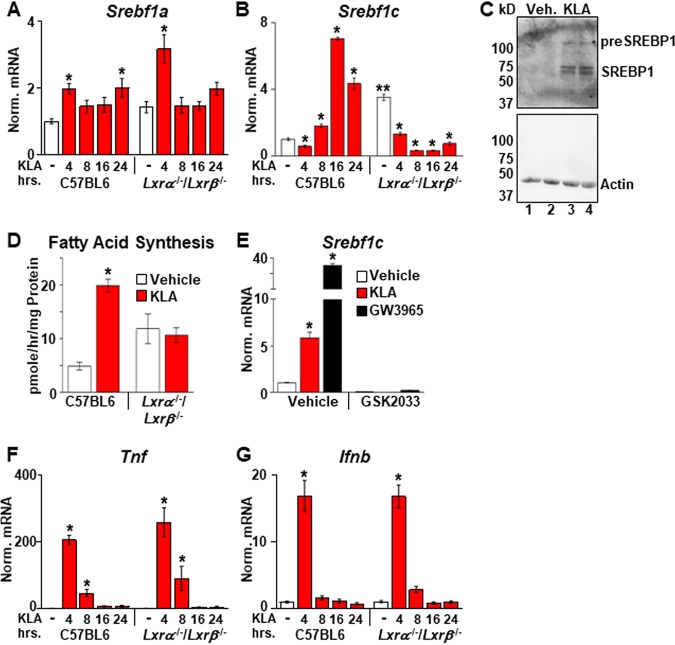
FIG 1.
TLR4 activation induces Srebf1c and Lxrα. (A, B, F, and G) C57BL/6 and Lxrα−/−/Lxrβ−/− BMDM were treated with the vehicle or 100 ng/ml KLA for the times shown. Following treatment, mRNA levels of Srebf1a (A), Srebf1c (B), Tnf (F), and Ifnb (G) were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized to the value for cyclophilin. *, statistically significant difference from the vehicle control within the same genotype; **, statistically significant difference between C57BL/6 and Lxrα−/−/Lxrβ−/− vehicle controls determined by 2-way ANOVA (P ≤ 0.05; n = 10). (C) C57BL/6 BMDM were treated with the vehicle or 100 ng/ml KLA for 16 h. Following treatment, nuclear extracts were prepared. SREBP1 and actin levels were examined by Western blotting as described in Materials and Methods. (D) C57BL/6 and Lxrα−/−/Lxrβ−/− BMDM were treated with the vehicle or 100 ng/ml KLA for 13 h and then labeled with [14C]acetate in the continued presence or absence of KLA for an additional 5 h. Fatty acids were extracted and quantified as described in Materials and Methods. *, statistically significant difference from the vehicle control within the same genotype determined by 2-way ANOVA (P ≤ 0.05; n = 8). (E) C57BL/6 BMDM were treated with the vehicle, 100 ng/ml KLA, or 100 nM GW3965 for 8 h and then treated for an additional 8 h with 1.0 μM GSK2033 in the continued presence of KLA or GW3965. Following treatment, mRNA levels of Srebf1c were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized to the value for cyclophilin. *, statistically significant difference between the vehicle control and treated groups determined by 2-way ANOVA (P ≤ 0.05; n = 8).