FIG 3.
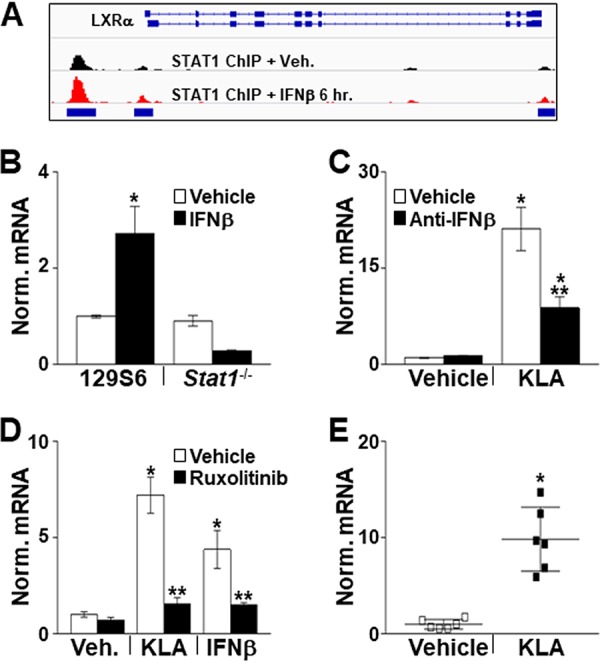
IFN-β induces Lxrα expression. (A) Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) screenshot demonstrating binding of STAT1 to the Lxrα promoter in vehicle- and IFN-β-treated BMDM. STAT1 ChIP-Seq data are derived from data reported under GEO accession number GSE33913 (34). (B) Control and Stat1−/− BMDM were treated with the vehicle or 100 ng/ml KLA for 8 h. Following treatment, Lxrα mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized to the value for cyclophilin. *, statistically significant difference from the vehicle control determined by 2-way ANOVA (P ≤ 0.05; n = 8). (C) THP-1 macrophages were treated with the vehicle or 10 ng/ml KLA for 8 h in the presence or absence of a neutralizing antibody against IFN-β. Following treatment, LXRα mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized to the value for cyclophilin. *, statistically significant difference from the vehicle control; **, statistically significant difference between KLA with and without anti-IFN-β determined by 2-way ANOVA (P ≤ 0.05; n = 8). (D) THP-1 macrophages were treated with the vehicle, 10 ng/ml KLA, or 20 ng/ml IFN-β for 8 h in the presence or absence of 1 μM ruxolitinib. Following treatment, LXRα mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized to the value for cyclophilin. *, statistically significant difference from the vehicle control; **, statistically significant difference between KLA or IFN-β with and without ruxolitinib determined by 2-way ANOVA (P ≤ 0.05; n = 8). (E) Male 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice were injected i.p. with the vehicle or 10,000 U of IFN-β. After 8 h, cells were recovered from the peritoneal cavity, RNA was isolated, and Lxrα mRNA levels were quantified by real-time PCR and normalized to the value for cyclophilin. *, statistically significant difference from the vehicle control determined by a Mann-Whitney test (P ≤ 0.05; n = 6). Data are means ± standard errors.
