Figure 2.
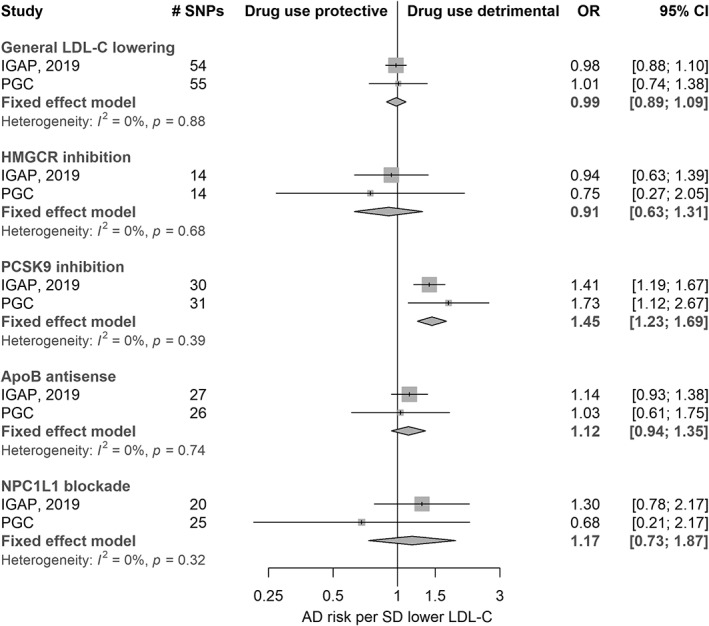
Meta‐analysis of Mendelian randomization estimates for Alzheimer disease (AD) risk according to a lifelong reduction in circulating low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL‐C) and exposure to the modulation of several related drug targets (n = 24,718 cases, 56,685 controls). The first group of results shows estimates for the effect of a general, long‐term reduction of LDL‐C (achievable by any means) on AD risk. The second to fifth group labels are representative of genetic variation at gene regions (HMGCR, PCSK9, APOB, and NPC1L1) that predict the effects of specific therapeutic target modulation, followed by example drug classes that affect these targets. CI = confidence interval; IGAP = International Genomics of Alzheimer's Project; OR = odds ratio; PGC = Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; SD = standard deviation; SNP = single nucleotide polymorphism.
