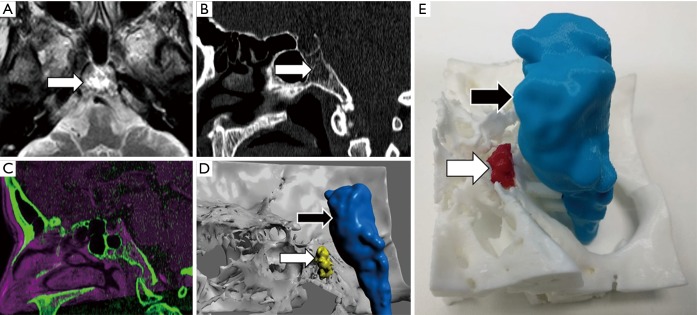
Figure 1.
Clival chordoma evaluation. A 45-year-old female that undergone MRI for migraine. (A) Axial T2-TSE sequence shows hyperintense lesion within clivus within punctate hypointensities (arrow). (B) Sagittal reconstruction of CT confirms the presence of a lytic lesion within clivus s with probably chondroid matrix inside (arrow). (C) Registration of both MRI and MCDT information allows delimitating brain tissue (magenta) using information from MRI and skull base structures (green) from CT. (D) The 3D virtual model and (E) the 3D printed model enable neurosurgeon to properly identify the location of chordoma (white arrow) concerning the brainstem (black arrow) and the rest of the skull base. This approach allows reduction of the risk of neurological complications before surgery or biopsy.