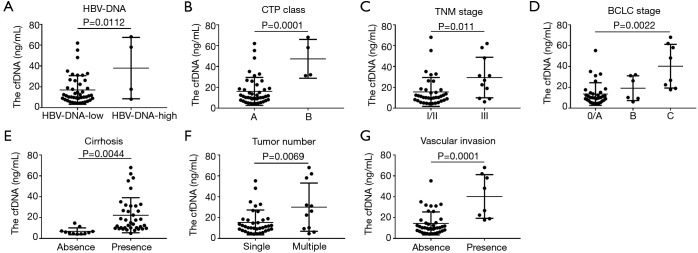
Figure 1.
The relationship between total plasma cfDNA and clinicopathological characteristics in HBV-related HCC patients. (A) The relationship between HBV-DNA and cfDNA; total plasma cfDNA in the low-HBV-DNA and high-HBV-DNA groups was 16.96±2.07 and 37.99±14.74 ng/mL (P=0.0112), respectively; (B) the relationship between CTP class and cfDNA; total plasma cfDNA in patients with CTP class A and class B was 16.11±2.02 and 47.33±9.30 ng/mL (P=0.0001), respectively; (C) the relationship between TNM stage and cfDNA; total plasma cfDNA in the patients with TNM stages I/II and III were 15.54±2.28 and 29.39±5.85 ng/mL (P=0.011); (D) the relationship between BCLC stage and cfDNA; total plasma cfDNA in the patients with BCLC 0/A stage, B stage and C stage were 13.56±1.87, 19.19±4.84 and 40.27±7.42 ng/mL (P=0.0022), respectively; (E) the relationship between liver cirrhosis and cfDNA; cfDNA concentrations in the absence and presence of liver cirrhosis were 6.84±0.99 and 22.24±2.77 ng/mL (P=0.0044), respectively; (F) the relationship between tumor number and cfDNA; the total plasma cfDNA concentrations in patients with single and multiple tumors were 15.35±1.96 and 30.03±6.98 ng/mL (P=0.0069), respectively; (G) the relationship between vascular invasion and cfDNA; total plasma cfDNA in HCC patients with and without vascular invasion was 14.40±1.75 and 40.27±7.42 ng/mL (P=0.0001), respectively. HBV, hepatitis B virus; CTP, Child-Turcotte-Pugh; BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer score; cfDNA, circulating cell-free DNA; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.