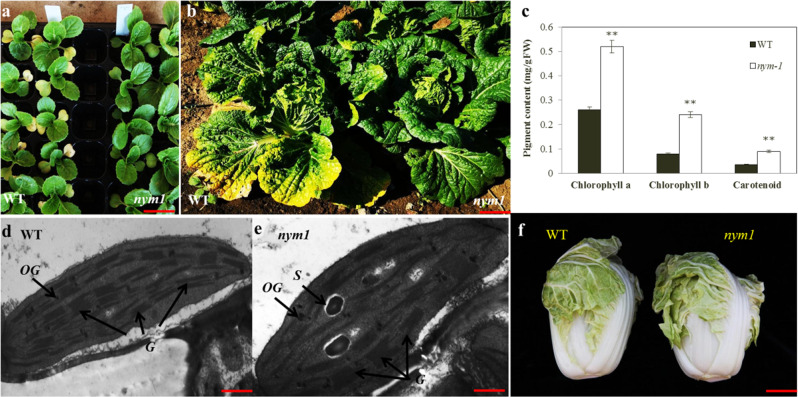
Fig. 1. Morphological characterizations of wild-type (“FT”) and nym1 mutant plants.
a Phenotypic characterizations of wild-type and mutant cotyledons. Plants 20 DAS (days after sowing). Bars = 3 cm. b Phenotypic characterizations of wild-type and nym1 rosette leaves. Plants were at the field-grown heading stage (50 DAS). Bars = 10 cm. c Pigment content of wild type and mutant bottom leaves. Plants 60 DAS. Ten plants from the wild type and “nym1” lines with the same growth potential were randomly selected. The second leaves from the bottom were sampled. **Significantly different at P = 0.01 by the t test. d, e Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of WT and mutant bottom leaves. The plant stage was the same as that for Fig. 1c. Three leaf specimens were sampled per plant. Fifteen sections were viewed by TEM. Twelve cells were examined and photographed per section. S starch granule, OG and arrow osmiophilic plastoglobuli, G granum. Bars = 5 μm. f Phenotypic characterizations of wild type and mutant leafy heads. Plants 70 DAS. Left panel: wild type; right panel: nym1. Bars = 7 cm.