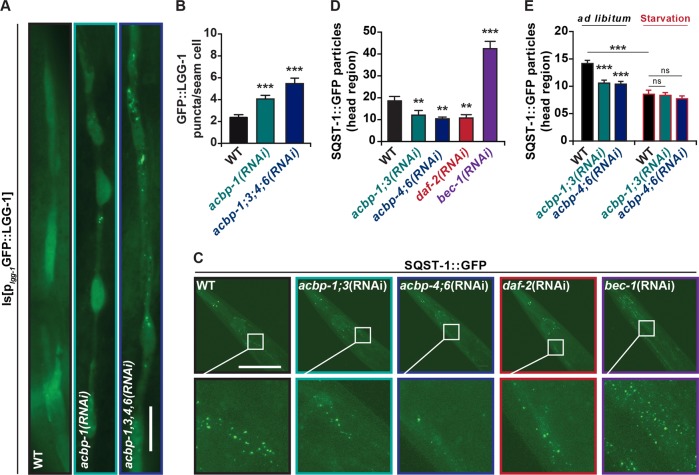
Fig. 2. Autophagy regulation by ACBP in C. elegans.
a Representative images of reporter worms expressing a GFP::LGG-1 fusion protein in the WT and genetic backgrounds lacking indicated acbp family genes (single acbp-1(sv62) and quadruple acbp-1(sv62);acbp-3(sv73);acbp-4(tm2896);acbp-6(tm2995) mutants. Scale bar, 20 μm. b Quantification of GFP::LGG-1 puncta per hypodermal seam cell in WT, acbp-1(sv62) and acbp-1(sv62);acbp-3(sv73);acbp-4(tm2896);acbp-6(tm2995) mutant animals (n = 25 worms). c Representative images of SQST-1::GFP reporter worms treated with known regulators of autophagy (daf-2 and bec-1), as well as indicated acbp RNAis. Scale bar, 100 μm. d Quantification of SQST-1/p62::GFP puncta in the head region in control and RNAis treated animals (n = 25 worms). e Quantification of SQST-1/p62::GFP puncta in the head region in control and RNAi treated animals fed ad libitum or upon 12 h of starvation (n = 25 worms). Quantitative results are reported as means ± SEM. Symbols indicate statistical (Student’s t-test) comparisons with controls (n.s, not significant; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). All experiments were repeated at least three times, yielding similar results.