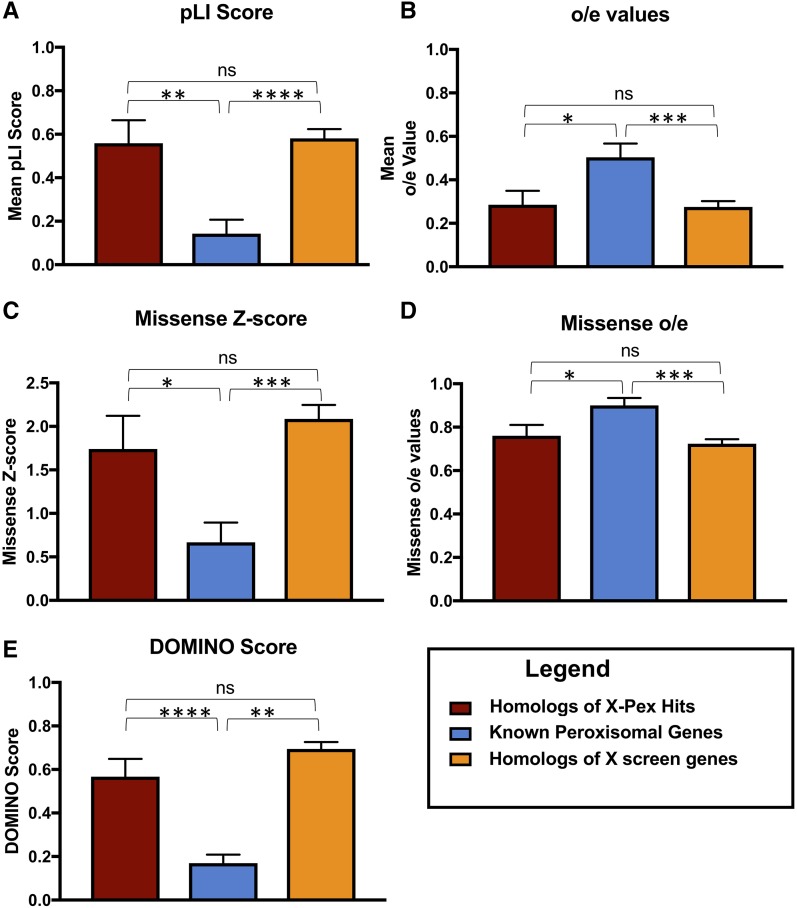
Figure 4.
Comparison of known human peroxisomal disease genes to the new X-Pex candidates. A. The Probability of Loss of Function intolerance score (pLi) calculated from human data from the gnomAD database (Lek et al. 2016). The X-Pex genes displayed a mean pLi score of 0.55 ± 0.11, n = 20, while the known peroxisomal disease genes had a mean pLi of 0.14 ± 0.06, n = 25, which was statistically significant (P = 0.0016) **. This was also compared to all the homologs of the X screen genes. B. The observed over expected (o/e) loss of function scores calculated from public human data from the gnomAD database. The X-Pex genes had a mean o/e score of 0.29 ± 0.06, n = 20, while the known peroxisomal disease genes had an o/e score of 0.50 ± 0.06, n = 25, which was statistically significant (P = 0.0218)*. This was also compared to all the homologs of the X screen genes. C. The missense constrain z-score calculated from public human data from the gnomAD database. The X-Pex genes had mean missense constrain z-scores of 2.16 ± 0.34, n = 20, while the known peroxisomal genes had z-scores of 0.67± 0.23, n = 25, which was statistically significant (P = 0.0005)***. This was also compared to all the homologs of the X screen genes. D. Missense constraint o/e scores calculated from public human data from the gnomAD database. The X-Pex genes had a mean o/e for missense variants of 0.73 ± 0.04, n = 20, compared to the known peroxisomal disease genes o/e score of 0.90 ± 0.03, n = 25, also statistically significant (P = 0.0025)**. This was also compared to all the homologs of the X screen genes. E. DOMINO scores calculated for the gene sets. The X-Pex gene set had a DOMINO score of 0.53 ± 0.08, n = 20, while the known peroxisomal disease genes had a mean DOMINO score of 0.17 ± 0.04, n = 24, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.0001)***. This was also compared to all the homologs of the X screen genes.