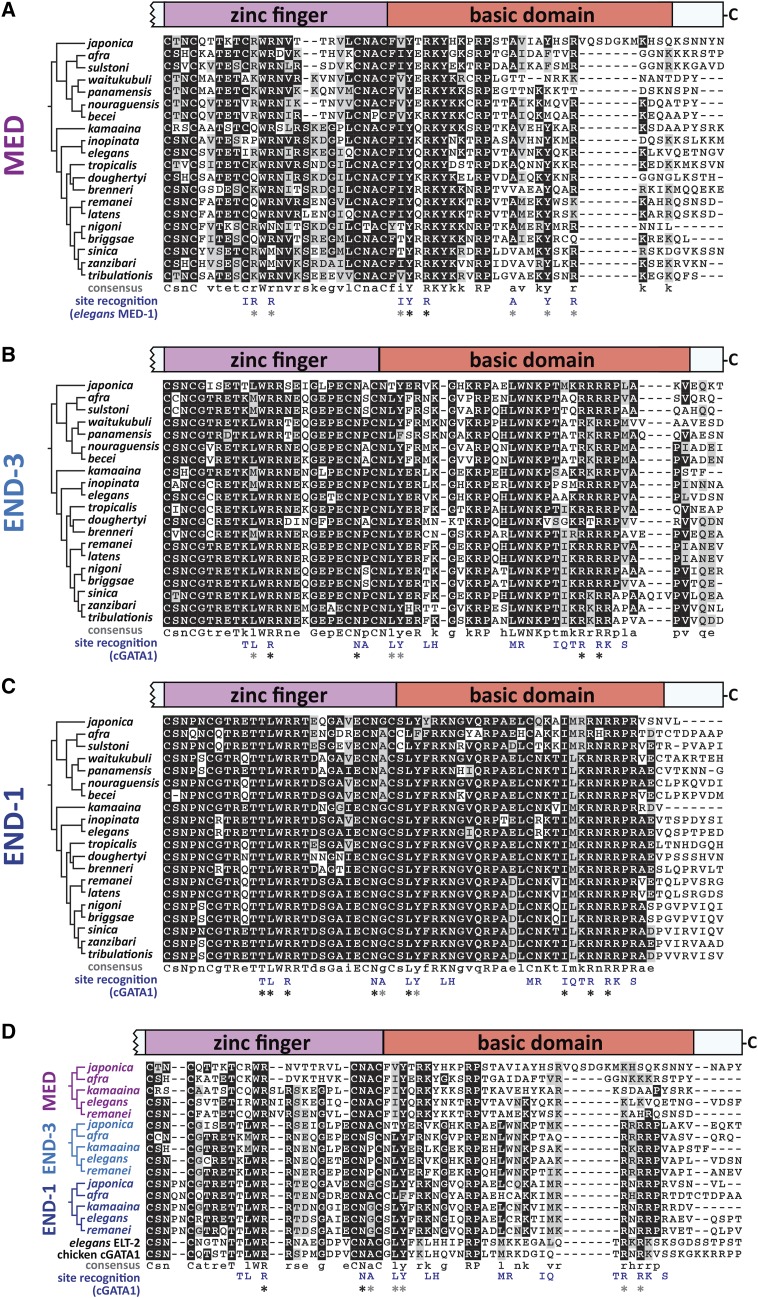
Figure 9.
DNA-binding domains (DBDs) and additional carboxyl amino acids aligned using MUSCLE (Edgar 2004). The zinc fingers and basic domains are shown for representative sequences of (A) MED, (B) END-3, (C) END-1, and (D) a representative subset of all three factors. Consensus sequences are shown below each alignment. The phylogeny of Stevens et al. (2019) is shown to the left of the species names for reference. Under the consensus sequences, the amino acids that mediate site recognition by the C. elegans MED-1 DBD for (A) and cGATA1 for (B), (C) and (D) are shown (Omichinski et al. 1993; Lowry et al. 2009). Asterisks show corresponding amino acids that are invariant (black) or are generally conserved (gray).