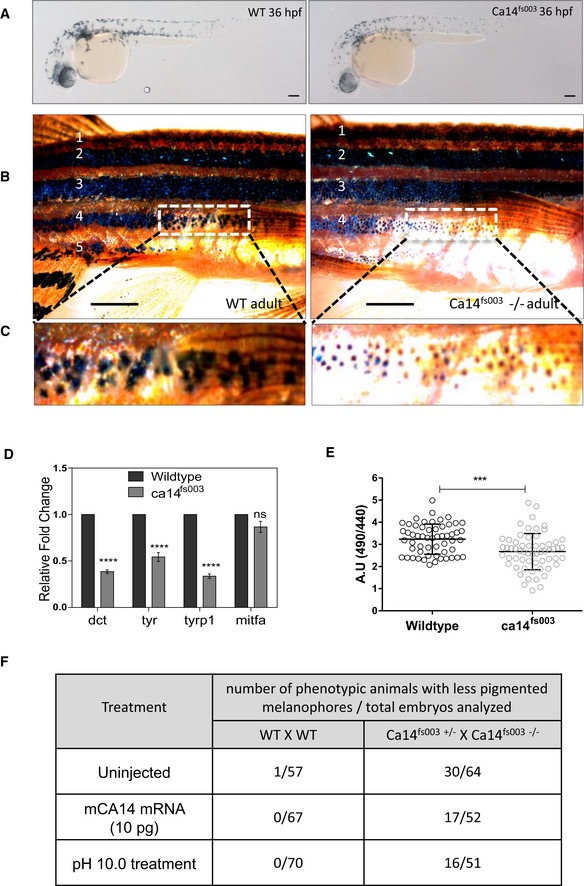
Brightfield images of the lateral view of CRISPR targeted mutant ca14
fs003 and control embryos at 36 hours post‐fertilization (hpf) in F2 generation fishes. Scale bar 100 μm.
Wild‐type and ca14
fs003−/− adult male animals were dark‐adapted for 24 h. Image of the lateral view was captured under identical lighting and image capture settings. Scale bar: 5 mm.
Zoomed up portion from the fourth lateral line demonstrates melanophores to be laden with less melanin content in the ca14 mutant animal.
qRT‐PCR quantification of pigmentation genes tyrosinase (tyr), dopachrome tautomerase (dct), tyrosinase‐related protein 1b (tyrp1b), and micropthalmia associated factor a (mitfa) between control and ca14
fs003 at 36 hpf, using rps11 gene as the normalization reference. While mitfa remains unaffected, all other pigmentation genes are downregulated in the absence of functional ca14. Bars represent mean ± SEM across n = 3 biological replicates.
Intracellular pHi probed by BCECF‐AM in ca14
fs003 and sibling control zebrafish embryos. Readings were obtained from trunk region melanophores. Bars represent mean ± SEM across n = 3 biological replicates, at least 10 embryos each. A decrease in the ratio indicates acidification of melanocytes.
Wild‐type as well as embryos obtained from the cross of ca14
fs003−/− and ca14
fs003+/− were left uninjected or treated with embyo water buffered at pH 10.0 (between 18 hpf till 36 hpf) or injected with 10 pg of in vitro transcribed mouse ca14 mRNA. Embryos were scored for pigmentation at 36 hpf. Ratios represent number of less pigmented phenotypic embroys to the total number of embryos scored. The proporition of less pigmented animals decreased upon mouse Ca14 mRNA injection as well as increased extracellular alkalinization.
‐test. ***
≤ 0.0001.