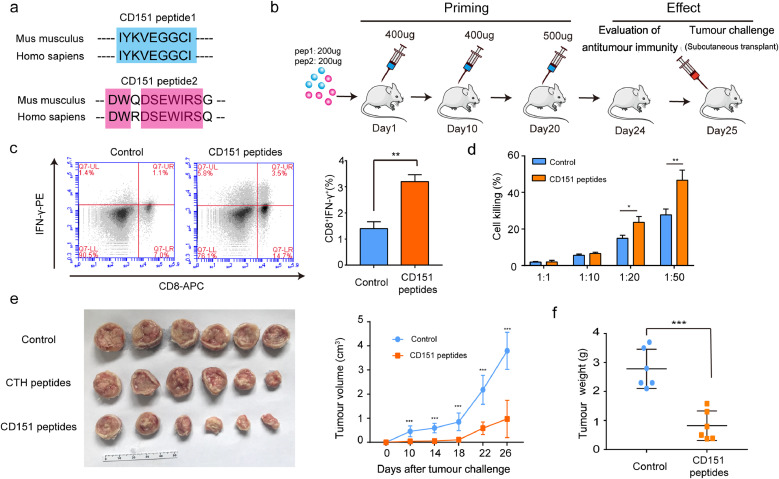
Fig. 3.
Peptides of CD151-triggered active immunity inhibited primary tumour growth of H22 hepatoma. (a) Two peptides derived from Mus musculus CD151 were synthesized according to MHC I binding and MHC I immunogenicity, and were blasted with sequences of Homo sapiens CD151. (b) Experimental schema depicting vaccination and tumour challenge schedule. Mice were vaccinated with CD151 peptides-Freund's adjuvant and received boost vaccinations 10 and 20 days later, followed by evaluation of anti-tumour immunity and primary tumour challenge. PBS with an equal volume of Freund's adjuvant was used as the control group (n = 10/group). (c) The scatter plots show the differences of spleen CD8+IFNγ+ T lymphocytes between control group and CD151 peptide immunisation group by FCM analysis. The percentage of CD8+IFNγ+ T lymphocytes is presented by the graph in the H22 models (n = 4/group). (d) To test the killing function of spleen lymphocytes, they were co-cultured with H22 tumour cells at different ratios of tumour cells to lymphocytes (1:1; 1:10; 1:20 or 1:50). The killing effect was measured by the LDH released (n = 4/group). (e) Image of primary tumours and growth curve of H22 hepatoma presented by tumour volume (n = 6/group). (f) Tumour weights at the end of experiment (n = 6/group). Results are representative of two independent experiments. P-values were determined by two-tailed Student's t-test (*, P<0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P <0.001).