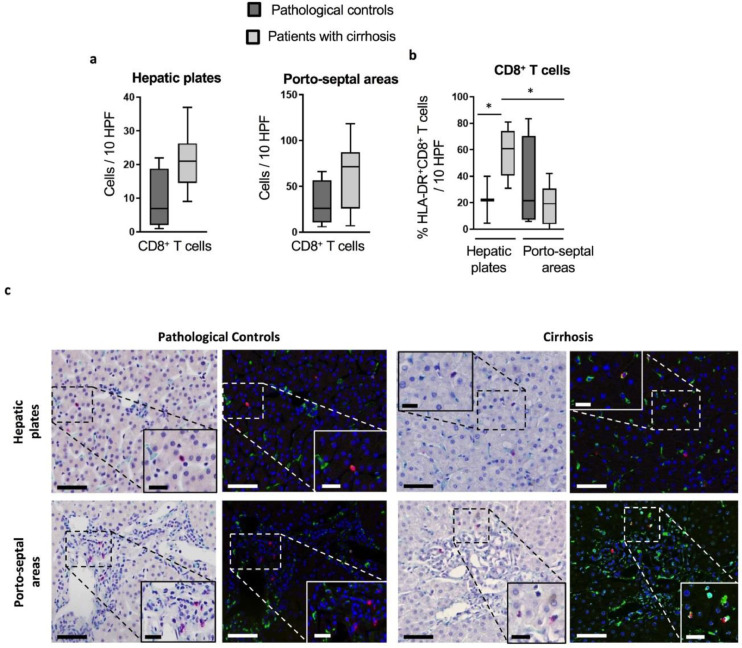
Fig 2.
Characterization of intrahepatic CD8+T cells in cirrhotic patients and pathological controls: Immunohistochemistry was performed on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded explanted liver tissue from cirrhotic patients (n = 8) and hepatic resection margins of colorectal metastases as pathological controls (n = 4). Micrographs were analyzed using the Nuance multispectral imaging system to obtain (a) the number of CD8+T cells/10 random high-power fields (HPF) in hepatic plates (left panel) and porto-septal areas (right panel), and (b) the proportion of HLA-DR+ cells within the intrahepatic CD8+T cell contingent per 10 random HPF.* p< 0.05. (c) Representative micrographs for CD8/HLA-DR double epitope enzymatic immunohistochemistry in pathological controls (left panel) and cirrhotic livers (right panel) (400x); left columns: bright field micrographs showing CD8+ cells in red, and HLA-DR+ cells in green, with hematoxylin as nuclear counterstaining; right columns: corresponding pseudo-fluorescent micrographs showing CD8+ cells in red, HLA-DR+ cells in green, nuclei in blue, and co-localization of CD8 and HLA-DR signals in yellow. (Scale bars: 50 μm for 400x magnification; 20 μm for insets). (Man-Whitney U test for comparison between cirrhotic patients and pathological controls; Wilcoxon signed-rank test for comparison between hepatic plates and porto-septal areas).