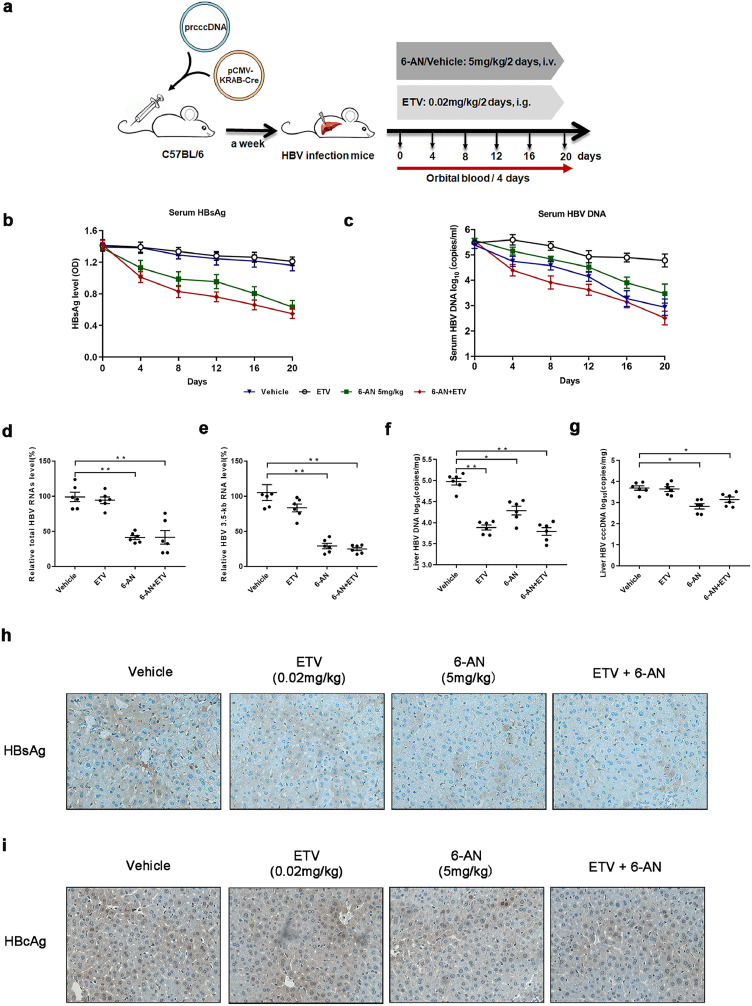
Fig. 7.
Combination treatment with 6-AN and ETV induced a profound reduction of both viremia and HBsAg levels in (r) cccDNA recombination mice. (a) Flow chart explaining the way and concentration of 6-AN and ETV administration as well as the intervals of orbital blood collection. The mouse model established by injecting prcccDNA and pCMV-KRAB-Cre from tail vein. The mouse model of HBV infection involving HBV recombinant (r) cccDNA constructed successfully were randomly assigned to 4 groups (n = 6 per group). 6-AN was dissolved and diluted in saline and tail intravenous injected at a dose of 0 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg once in two days. ETV was dissolved in water by administering oral doses at 0.2 mg/kg/2day. Blood samples were taken every 4 days until the 20th day. (b) HBsAg were determined in serum during the treatment by ELISA. Shown are mean ratio to baseline values ± standard error from six mice. (c)The serum level of HBV DNA was extracted and analyzed by absolute quantification PCR. Shown are mean values ± standard error from six mice. At day 20, All animals from each group were sacrificed to harvest the liver samples. Hepatic HBV DNA, HBV cccDNA, total HBV RNAs and 3.5-kb RNA and immunohistochemistry examination of HBsAg were determined in those mice tissues after 6-AN treatment. (d-e) Relative real-time PCR was subjected to detect the total HBV RNAs (d) and 3.5-kb RNA (e) levels, the mRNA level of β-actin was used as an internal control. (f) Liver HBV DNA was analyzed by absolute quantification PCR. (g) Liver HBV cccDNA was analyzed by absolute quantification PCR, using cccDNA-specific primers. (h-i) Representative images of immunohistochemistry of HBsAg (h) and HBcAg (i) in liver tissue. (*P < 0.05; ⁎⁎P < 0.01; n.s., not significant).