Fig. 1.
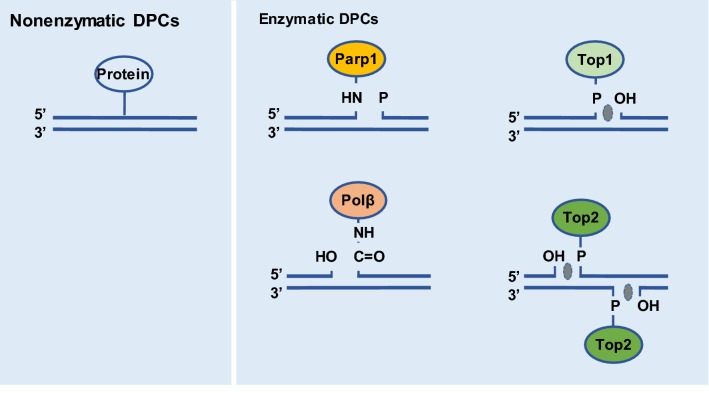
DPCs can be categorized as nonenzymatic or enzymatic based on the properties of the cross-linked proteins. Any proteins located in the vicinity of DNA can result in nonspecific DPCs triggered by various agents, including reactive compounds like aldehydes, metal ions, and several types of radiation. These are defined as nonenzymatic DPCs. Also, many DNA-related enzymatic reactions produce intermediates in which transient covalent linking between DNA and the enzyme occurs. Enzymes, such as DNA TOPs, DNA polymerases, and DNA methyltransferases, can be trapped and therefore form stable DPCs under certain circumstances. These are defined as enzymatic DPCs