Fig. 7.
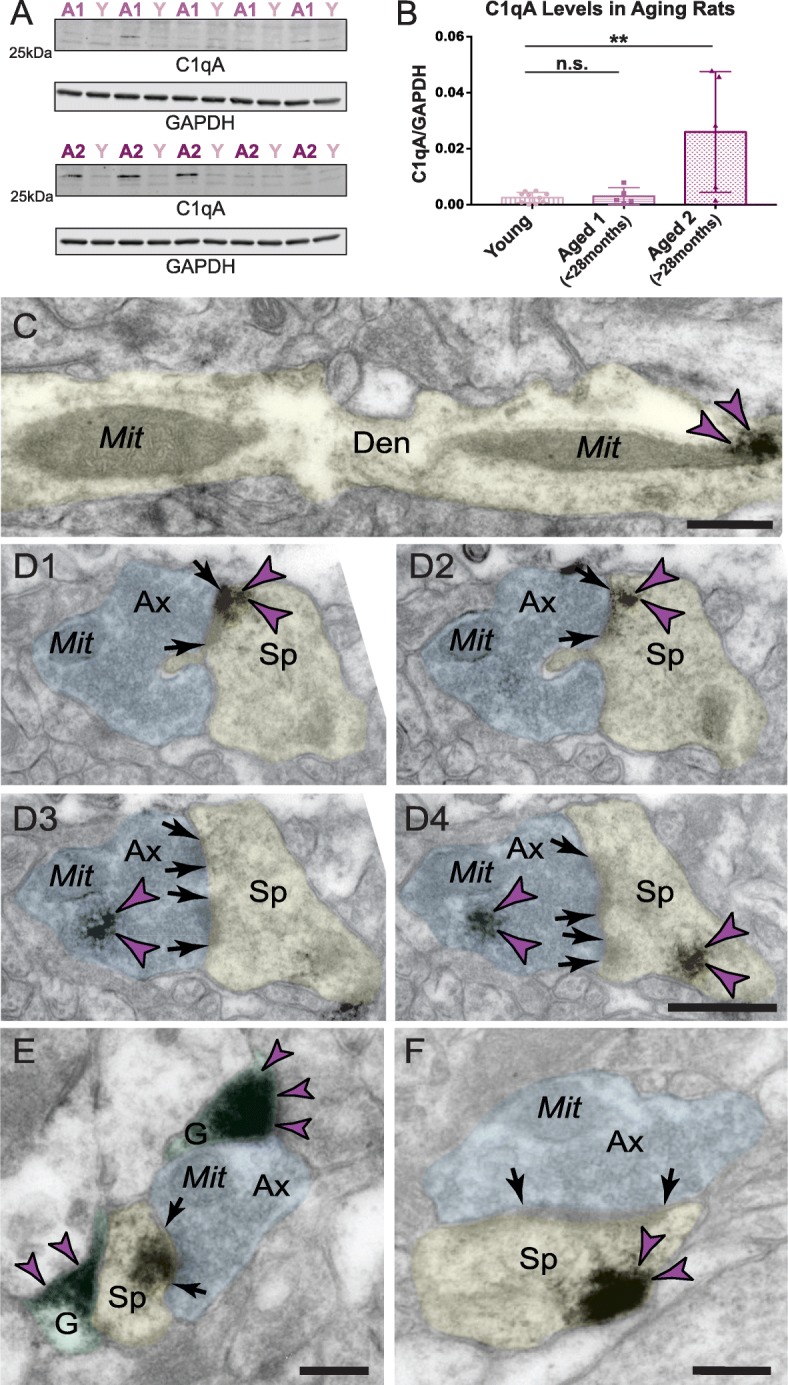
Age-related alterations in C1q protein in rat medial PFC. Biochemical characterization of C1qA in the rat frontal cortex. a Triton-soluble fractions from rat frontal cortex blocks were immunoblotted for C1qA and GAPDH. Lane labels are color-coded by age group; Y = young, ~ 3.5 months (n = 10); A1 = aged < 28 months (n = 5); A2 = aged > 28 months (n = 5). b Quantification of C1qA increase in the rat frontal cortex in the most advanced age group. Dunnett’s multiple comparison test to the young age group (adjusted p values: Y vs. A1 p = 0.995, Y vs. A2 **p = 0.002). c Significant labeling of C1q within dendritic shafts in postsynaptic compartments in aged rat mPFC layer II/III in close proximity to MOAS profiles. d1–d4 Intra-neuronal pre- and postsynaptic labeling of C1q protein in axospinous asymmetric synapse in aged rat mPFC layer II/III. The C1q immunopositive axospinous synapse is visualized in serial sections in rat mPFC sections. Postsynaptic labeling of C1q protein is observed in association with the plasma membrane (d1–d2) in perisynaptic locations and likely in association with the spine apparatus (d4) in different subcellular microdomains. Presynaptic labeling of C1q protein is observed in association with synaptic vesicles (d3, d4). e C1q labeling is observed in glial leaflets ensheathing the axospinous glutamatergic-like asymmetric synapses. C1q protein is also visualized within the glutamatergic-like PSD per se in the postsynaptic compartment. f Postsynaptic labeling of C1q within dendritic spines in extrasynaptic locations in association with the plasma membrane near the PSD. Synapses are between arrows. Color-coded arrowheads (purple) point to C1q immunoreactivity. Profiles are pseudocolored for clarity. Ax, axon; Den, dendrite; Sp, spine; Mit, mitochondria; G, glia. Scale bars, 200 nm
