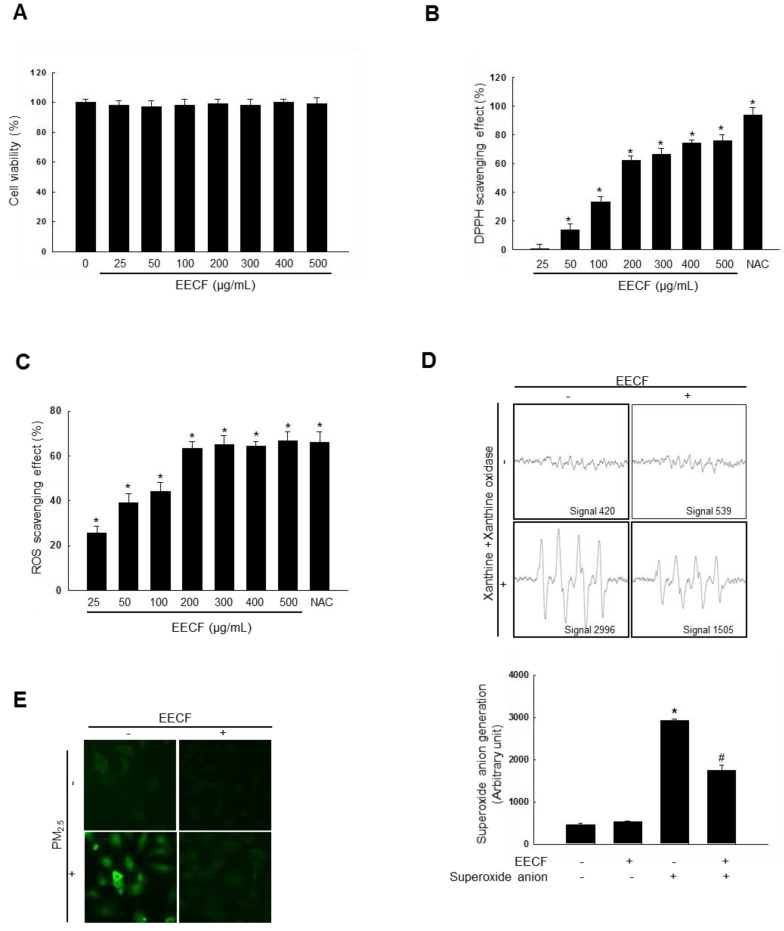
Figure 1.
Ethanol extract of C. officinalis fruit (EECF) reduced ROS generation. (A) MTT assay was used to assess cell viability of EECF (0, 25, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 µg/mL)-treated HaCaT cells for 24 h. (B) Radical-scavenging effects of EECF were investigated using DPPH assay. *p < 0.05 compared with control. (C) Intracellular ROS level that generated by H2O2 (1mM), was detected using spectrophotometer after DCF-DA staining. NAC is the positive control. *p < 0.05 compared with control. (D) Superoxide anion reducing ability of 200 µg/mL EECF was investigated using xanthine/xanthine oxidase system. *p < 0.05 and #p < 0.05, compared with control and superoxide anion-treated group, respectively. (E) Effect of EECF on PM2.5-induced intracellular ROS generation was assessed using DCF-DA staining by confocal microscopy.