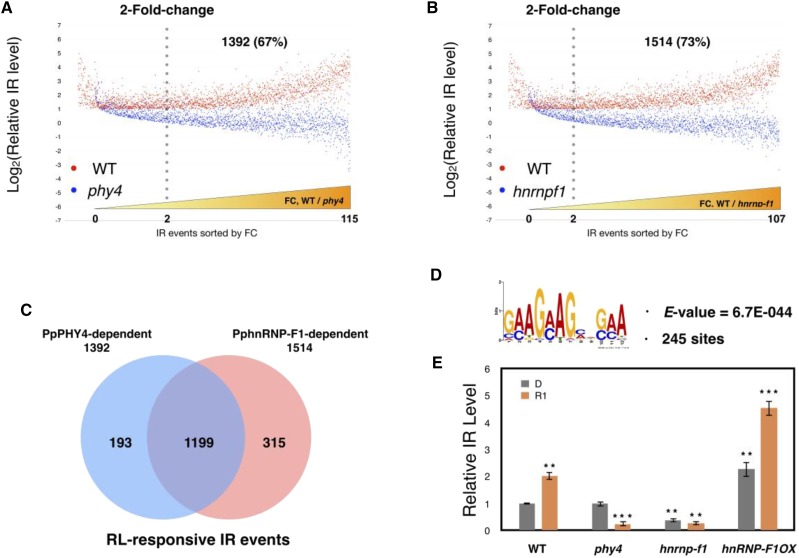
Figure 2.
PpPHY4 and PphnRNP-F1 cooperatively control RL-responsive IR. A and B, Analysis of 2056 RL-induced IR events. Profiles of the relative levels of RL-responsive IR events in wild type (WT) and PpPHY4-knockout mutant (phy4; A) or PphnRNP-F1-knockout mutant (hnrnp-f1) plants (B) Log2-transformed relative IR levels of the corresponding events in wild type and phy4 or hnrnp-f1 are shown in the order of fold-change (FC; WT/phy4). C, Venn diagram of PpPHY4-dependent and PphnRNP-F1-dependent RL-induced IR events. D, The repetitive GAA motif is enriched in 1199 RL-responsive IR events cooperatively regulated by PpPHY4 and PphnRNP-F1. The E-value (indicating the statistical significance of the motif) is shown under the motif, and the total number of sites is indicated. E, Relative IR levels of PpRPS8 (Pp3c13 20020) intron 4 in wild type, phy4, hnrnp-f1, and PphnRNP-F1 overexpression lines (PphnRNP-F1-OX) detected by RT-qPCR. Samples were collected from dark-grown protonemata (D) and protonemata treated with RL for 1 h (R1). Relative IR level was calculated according to a previous study and tested in three independent biological replicates with primer sets designed for IR splice variant and total transcripts. Error bars show the SEM (n = 3 biological replicates; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t test).