Figure 1.
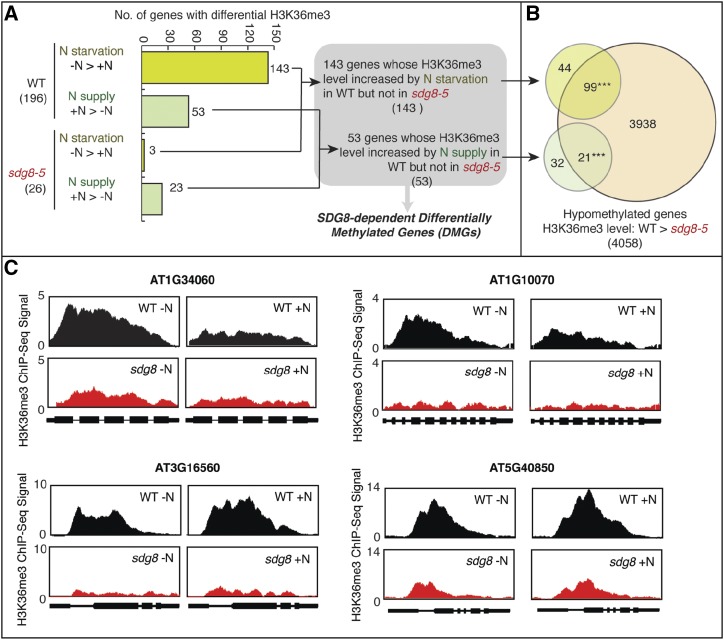
N-responsive H3K36 methylation is attenuated in the sdg8-5 deletion mutant. A, The comparison of genome-wide H3K36me3 patterns between N-supplied (+N) and N-depleted (−N) wild-type (WT)plants identified 196 genes with differentially methylated H3K36, including 143 genes that have higher H3K36me3 in −N than in +N, and 53 genes that have higher H3K36me3 in +N than in −N. In the sdg8-5 mutant, only three genes were identified to have higher H3K36me3 in −N than in +N, and 23 genes were identified to have higher H3K36me3 in +N than in −N. There is no overlap between the genes identified in the wild type and that identified in the sdg8-5 mutant. Therefore, we identified 143 genes that gain H3K36me3 in N-starvation condition in the wild type but not in the sdg8-5 mutant, and 53 genes that gain H3K36me3 in N-supplied condition in the wild type but not in the sdg8-5 mutant. B, Overlaps of the two groups of differentially methylated genes with the H3K36 hypomethylated genes (i.e. genes with less H3K36me3 in the sdg8-5 mutant compared to wild type) are shown in the Venn diagram. Asterisks indicate a significant overlap: ***P < 0.001 determined using the software Genesect. C, Exemplary genes show H3K36me3 responses to nitrate level change in the wild type but not in the sdg8-5 mutant.