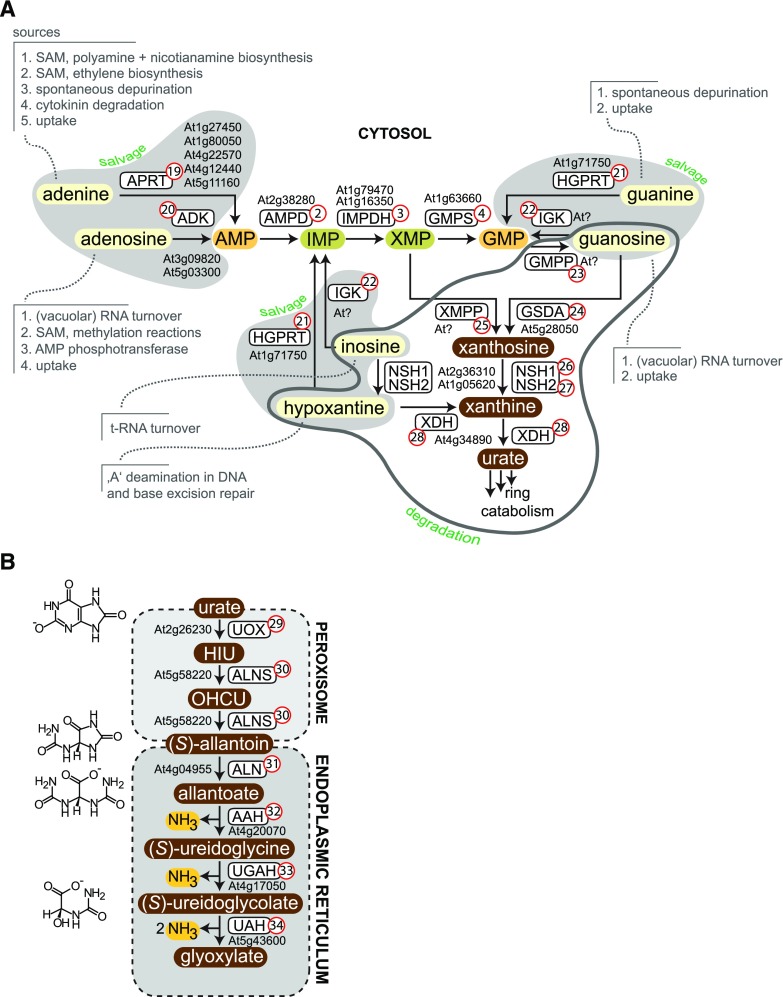
Figure 5.
Salvage and degradation of purines. A, Reactions of purine nucleobase and nucleoside salvage, as well as purine nucleotide degradation, which overlaps partially with GMP synthesis. The salvage pathways are highlighted by light gray shading, and the degradation reactions are encircled in dark gray. Metabolites that can only undergo degradation and cannot be salvaged are shown with brown shading. B, Purine ring catabolism. The transport steps for urate and (S)-allantoin are not shown explicitly. APRT (19), adenine phosphoribosyltransferase; ADK (20), adenosine kinase; AMPD (2), AMP deaminase; IMPDH (3), IMP dehydrogenase; GMPS (4), GMP synthetase; HGPRT (21), hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; IGK (22), inosine guanosine kinase; GMPP (23), GMP phosphatase; GSDA (24), guanosine deaminase; XMPP (25), XMP phosphatase; NSH1 (26), nucleoside hydrolase 1; NSH2 (27), nucleoside hydrolase 2; XDH (28), xanthine dehydrogenase; UOX (29), urate oxidase; ALNS (30), allantoin synthase; ALN (31), allantoinase; AAH (32), allantoate amidohydrolase; UGAH (33), ureido-Gly aminohydrolase; UAH (34), ureidoglycolate amidohydrolase.