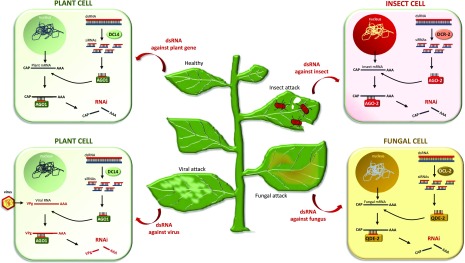
Figure 3.
Exogenous application of RNA molecules into plants against various targets, such as endogenous plant genes, viruses, insects, and fungi. In the first two cases, RNAi should take place inside the plant cell. Thus, the most suitable application method is high-pressure spraying, which allows symplastic RNA delivery. In contrast, in the cases of insects and fungi, RNAi takes place inside the insect and fungal cells, which thus need to uptake intact dsRNA (unprocessed by the plant DCLs) to achieve efficient RNAi. Hence, in these cases, trunk injection, petiole absorption, and/or low-pressure spraying (wherein RNA stays on the leaf surface) are the most suitable methods, because these methods do not result in symplastic RNA delivery. Importantly, although trunk injection and/or petiole absorption is the ideal method for xylem-feeding and/or chewing insects, the spraying method would be more suitable for phloem-feeding insects (e.g. aphids).