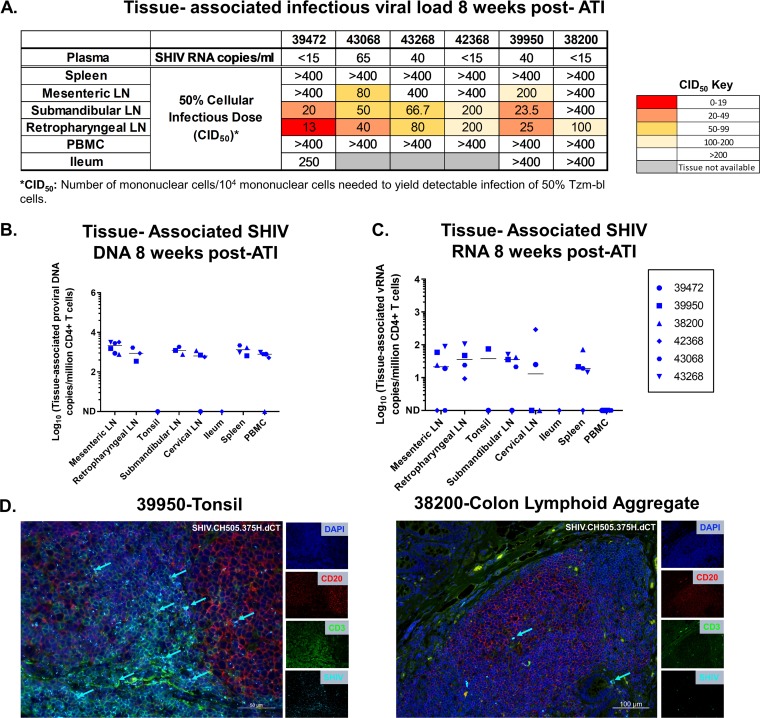
FIG 4.
Tissue-associated infectious virus load upon ATI in mononuclear cells isolated from PBMCs and lymphoid and gastrointestinal tissues of adult RMs intravenously infected with SHIV.CH505.375H.dCT. (A) Tissue-associated infectious SHIV.CH505.375H.dCT titers measured through tissue mononuclear cell coculture with TZM-bl reporter cells. The reported titers represent the estimated minimum number of mononuclear cells per 104 mononuclear cells required to yield detectable infection of 50% of TZM-bl cells (CID50). (B and C) CD4+ T cell-associated proviral DNA (B) and viral RNA loads (C), reported as the copy number per million CD4+ T cells in PBMCs and lymphoid and gastrointestinal tissue mononuclear cells. Each symbol represents one individual monkey at necropsy (week 32 postinfection). Medians are indicated as horizontal lines on the dot plots. (D) Tonsil and colon sections from the SHIV.CH505.375H.dCT-infected adult RM (animal 39950) that demonstrated the highest peak plasma VL postrebound (13,000 vRNA copies/ml plasma). Tissue sections were stained with the nuclear marker DAPI (dark blue) to identify cells and with antibodies specific for CD3 (green) and CD20 (red). Virus-infected cells were identified by in situ hybridization (cyan). Each panel consists of a larger image with the overlay of all markers and 4 smaller side panels of the same field for each individual channel. Arrow colors correspond to the color for the indicated marker. The large image has a scale bar in the lower right corner.