Figure 2.
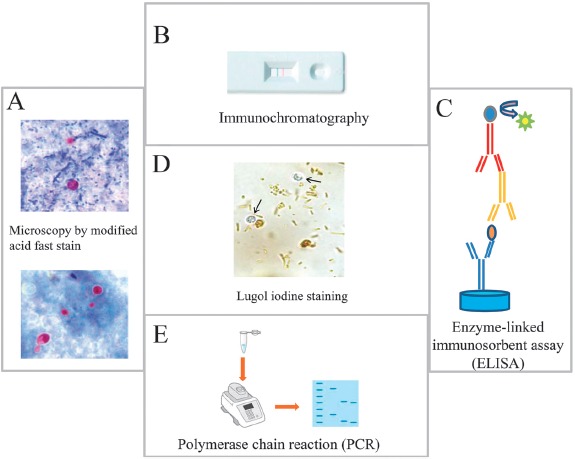
Principal methods used for the detection of Cryptosporidium in stool samples. (A) Microscopic identification of Cryptosporidium cysts stained by modified Ziehl–Neelsen stain. Upper panel, the oocysts stain bright red against a background of blue-green fecal debris and yeasts; lower panel, colorless oocysts that have been associated with resolving infection. (B) Immunochromatographic assay for detecting Cryptosporidium oocysts in stool samples, (C) ELISA assay for the detection of Cryptosporidium antigen in stool samples, and (D) Cryptosporidium oocysts (arrows) do not stain with Lugol's iodine solution. Oocysts appears similar to yeasts but colorless. (E) PCR detection of Cryptosporidium
