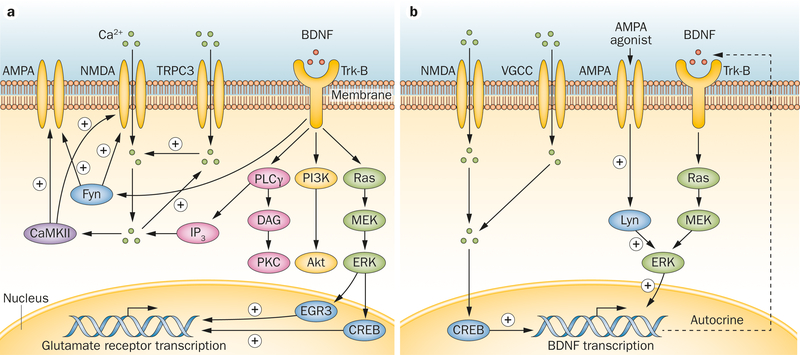
Figure 2 |.
Schematic diagram of the interaction between BDNF and glutamate receptors. BDNF binds to the extracellular domain of Trk-B receptor, activating an intracellular signalling cascade that includes PI3K–Akt, Ras–MAPK and the PLCγ–Ca2+ pathways. a | BDNF can facilitate NMDA receptor and AMPA receptor signalling through Fyn and PLCγ-Ca2+ and CaMKII pathways. NMDA and AMPA receptor expression is enhanced through the BDNF-mediated MAPK pathway. b | Glutamate receptors modulate BDNF signalling through Lyn and calcium signalling, which further induces BDNF expression and secretion in an autocrine fashion. Abbreviations: Akt, protein kinase B; AMPA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CREB, cAMP-responsive element-binding protein; DAG, diacylglycerol; EGR3, early growth response protein 3; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Fyn, tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; Lyn, tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; NmDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ; Ras, Ras small GTPase family proteins; Trk-B, tropomyosin-related kinase B; TRPC3, short transient receptor potential channel 3; VGCC, voltage-gated calcium channel.