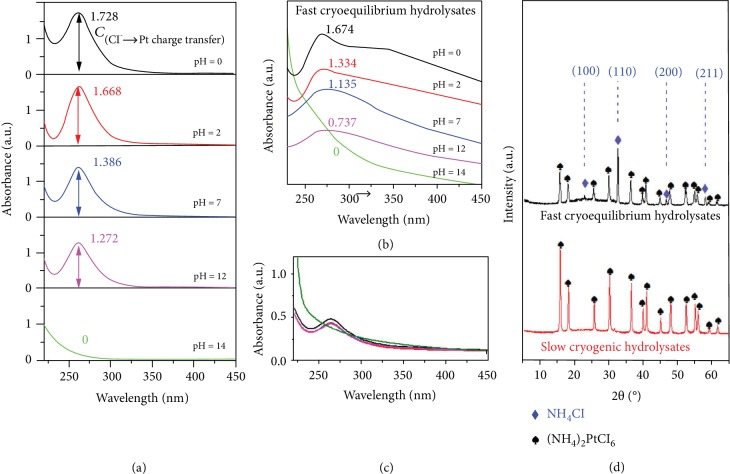
Figure 2.
Detailed structural characterizations of fast and slow cryogenic hydrolysates. (a) UV-vis absorption spectra of (NH4)2PtCl6 aqueous solutions (0.1 mg ml−1) with different pH values (from 0 to 14), clearly indicating that the [PtCl6]2- ion undergoes deep hydrolysis with increasing pH values. (b, c) UV-vis adsorption spectra of fast cryoequilibrium hydrolysates (b) and slow cryogenic hydrolysates (c) obtained from the (NH4)2PtCl6 solution with different pH values (from 0 to 14), showing that the hydrolysates at the different dynamic equilibrium states could be well maintained through fast cryogenic treatment. (d) XRD patterns of fast cryoequilibrium hydrolysates and slow cryogenic hydrolysates confirm the existence of NH4Cl in the obtained fast cryoequilibrium hydrolysates.