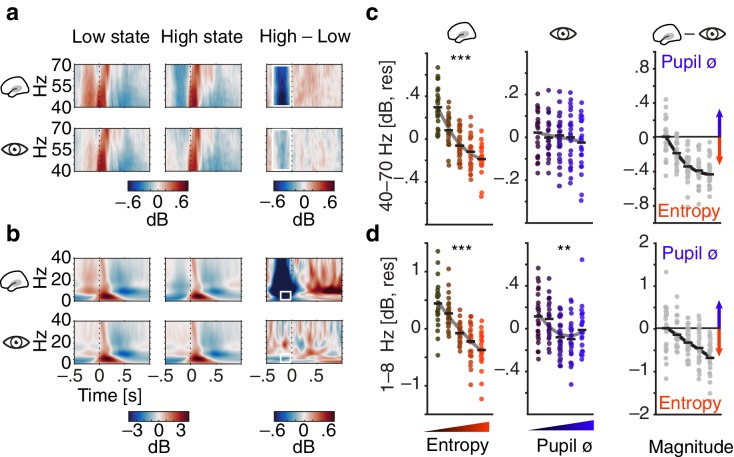
Figure 3. Contribution of pre-stimulus entropy and pupil size to ongoing auditory cortical EEG activity.
(a) Grand average gamma power across time (40–70 Hz, baselined to the whole trial average, in dB) for low states (left), high states (middle) and the difference of both (right). Entropy states are shown in the upper panel, pupil states in the lower panel. Dashed line represents tone onset, white rectangle outlines the pre-stimulus window of interest. (b) As in (a) but for 0–40 Hz. (c) Mean-centred single subject (dots) and grand average gamma power (black lines) in the pre-stimulus time-window (−0.4–0 s), residualized for baseline entropy and pupil size, shown for five bins of increasing pre-stimulus entropy (left) and pupil size (residualized for entropy baseline and pre-stimulus entropy, middle). Grey line represents average fit, red colours show increasing entropy, blue colours increasing pupil size. Effects of entropy and pupil size are contrasted in the right panel. (d) As in (c) but for low-frequency power (1–8 Hz). Note the different y-axis range between entropy and pupil effects. All binning for illustrational purposes only. ***p<0.0001, **p<0.001.
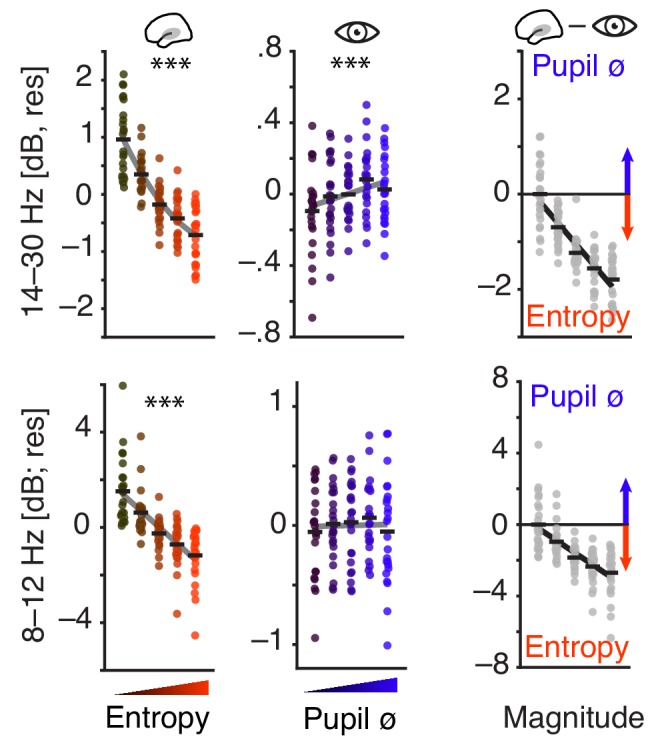
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Ongoing activity in the alpha and beta band as a function of EEG entropy and pupil size.