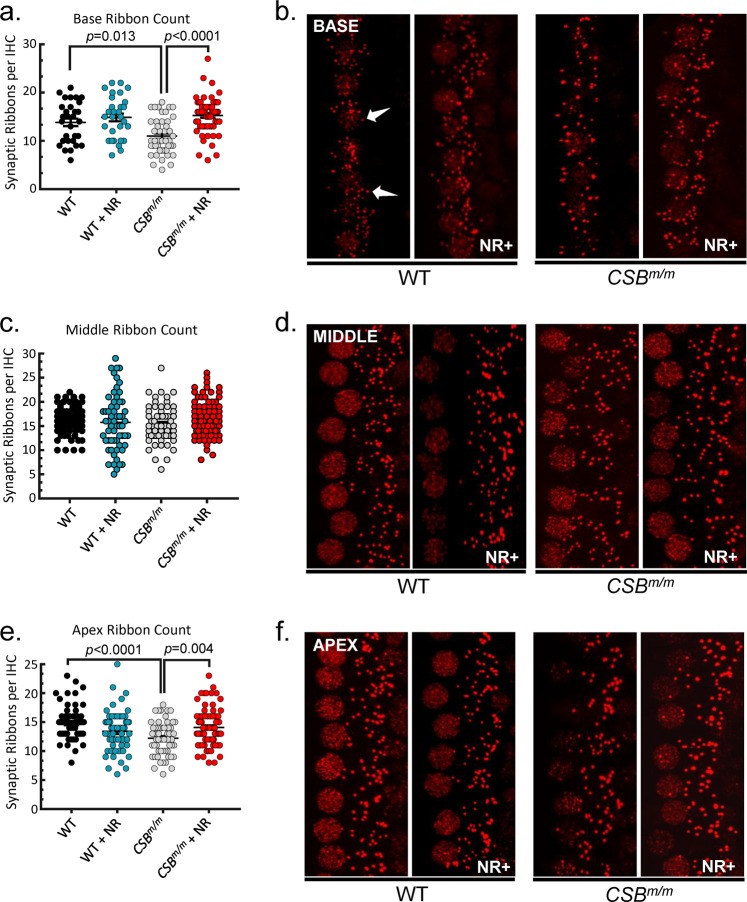
Fig. 5. NR enhances synaptic ribbon count per inner hair cell in the base and apex regions in CSBm/m mice cochlea.
a, c, e The average synaptic ribbon count per inner hair cell in the cochlea base region (a), middle region (c), and apex region (e). The average number of ribbons is reduced in the base turn of the cochlea in CSBm/m mice relative to WT at 6.5 weeks of age. However, this effect is prevented by NR treatment. A similar change is observed in the apical turn but not in the middle region of the cochlea. b, d, f Representative image of immunostaining for synaptic ribbons (red, anti-Ctbp2) of cochlear base segments (b), middle segments (d), and apex segments (f). A magnification of 40× was used for all images that are oriented such that the base of each hair cell is located on the right side of the image. Hair cell nuclei, which are also labeled with anti-Ctbp2, are located on the left side. Each individual puncta represents a single synaptic ribbon (arrows). Fifteen cells per region per mouse are used for quantification; 12 mM NR in drinking water for 10 days was used for intervention (CSBm/m (N = 4); CSBm/m + NR (N = 5); WT (N = 4); WT + NR (N = 4); mean ± S.E.; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test was used to determine significant difference).