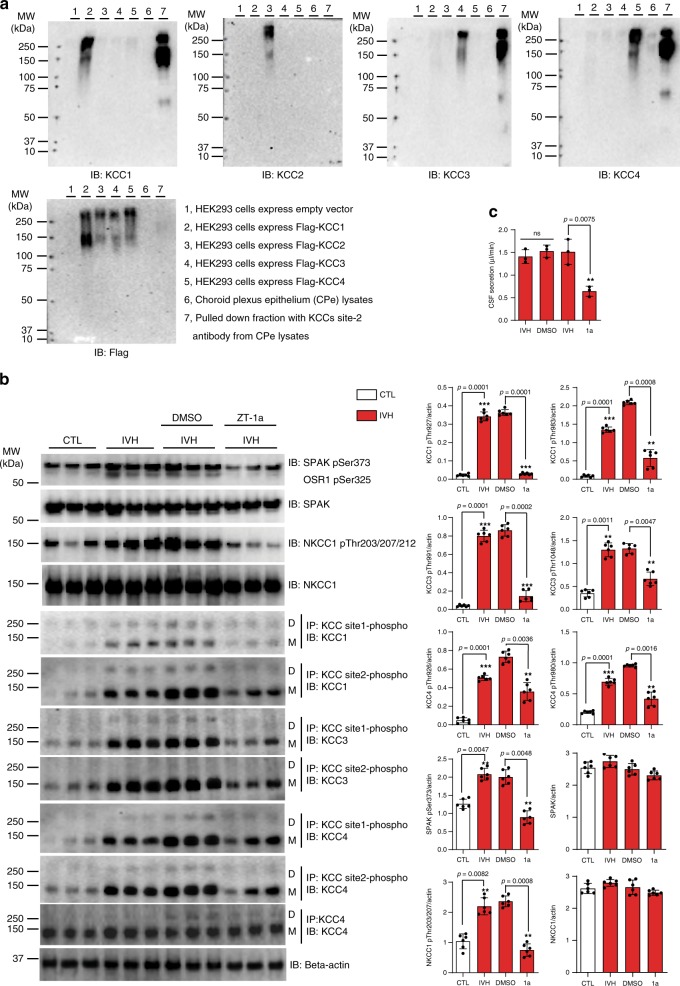
Fig. 4. ZT-1a decreases SPAK–CCC phosphorylation in hemorrhagic hydrocephalus.
a Representative immunoblots verify antibody specificity. KCC1–4 were expressed in HEK-293 cells. KCC site-2 phospho-antibody pull- down fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot with antibodies targeting specific transporters (n = 3). b Effect of ZT-1a (ICV, 10 mmol) on IVH-induced phosphorylation of SPAK/OSR1, NKCC1, and KCC4 in CPE, as measured in control rats (CTL) and in rats 48 h post IVH treated with ZT-1a or vehicle (n = 3). CPE lysates were harvested and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblot (IB) with the indicated antibodies. D, dimeric KCCs; M, monomeric KCCs. Quantitation of actin-normalized choroid plexus ion transporter phosphorylation is presented in control rats (CTL) and rats 48 h after experimental IVH in the presence or absence of ZT-1a or vehicle (n = 3). ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 versus control rats [by one-way ANOVA with post hoc testing (error bars represent the mean ± SEM)]. c Effect of SPAK inhibition by 10 µM ZT-1a on IVH-induced CSF hypersecretion by CPE (n = 3). The rate of CSF production (µL/min) is presented as means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01 versus baseline IVH [one-way ANOVA with post hoc testing (error bars represent the mean ± SEM)].