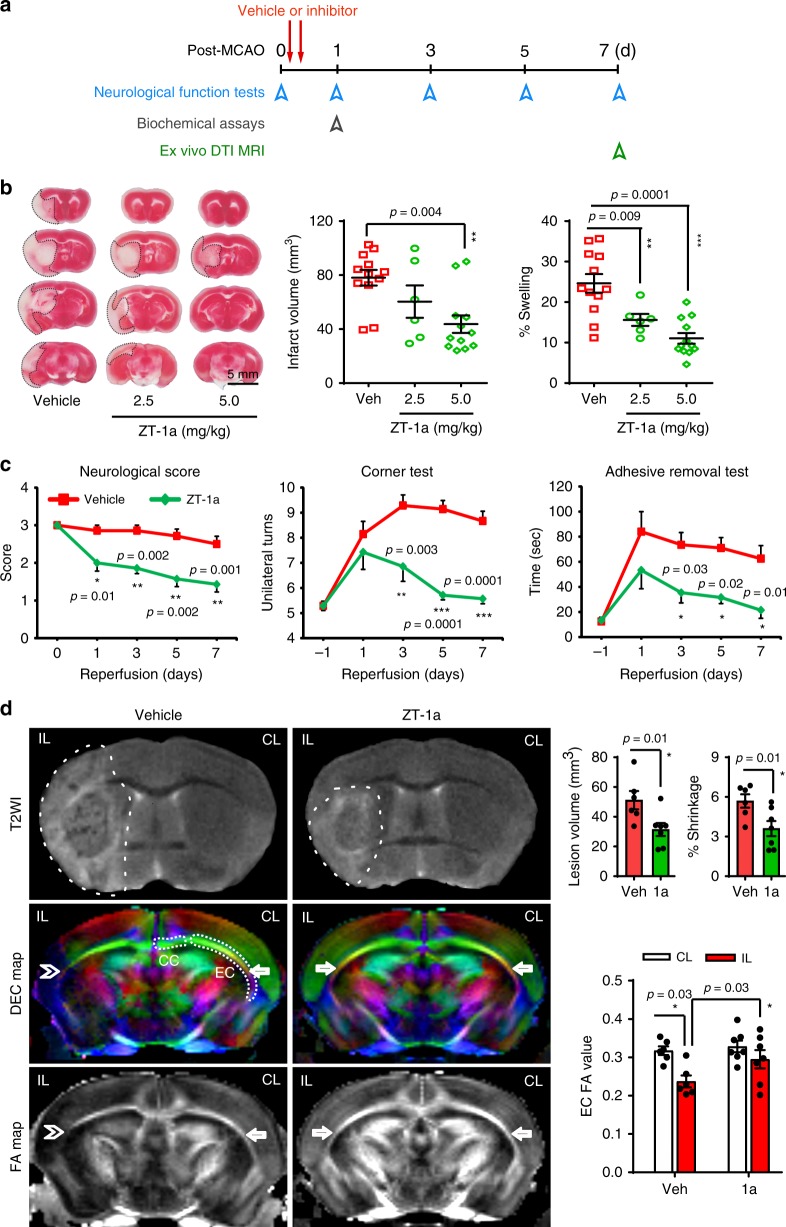
Fig. 7. ZT-1a decreases brain injury after ischemic stroke.
a Experimental design of ischemic stroke study. Vehicle or ZT-1a is administered at 3 and 8 h post tMCAO. b Representative images and quantitation of infarct volume and hemispheric swelling in TTC-stained coronal sections of mouse brains 24 h post tMCAO. Vehicle (DMSO, 2 ml/kg) or ZT-1a (2.5 or 5.0 mg/kg) were administered via intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) with initial half-dose at 3 h and second half-dose at 8 h post reperfusion. Data are mean ± SEM, male mice, n = 12 (vehicle), 6 (ZT-1a 2.5), and 12 (ZT-1a 5.0). ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01 versus vehicle-control mice, one-way ANOVA. c Neurological deficit scores, corner tests, and adhesive tape removal tests of mice 1 day before tMCAO (–1) and at days 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7 post tMCAO. Vehicle (DMSO, 2 ml/kg) or ZT-1a (5.0 mg/kg) were administered as described in b. Data are means ± SEM, n = 7 for each group (male 4, female 3). ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 versus the respective vehicle control. d Representative images of T2WI, directionally encoded color (DEC), and fractional anisotropy (FA) maps of ex vivo brains from the same cohort of mice at 7 days post tMCAO, as described in c. Arrow marks EC (external capsule); double arrowhead marks damaged EC; CC: corpus callosum. Bar graphs display quantitation of brain lesion volume, brain atrophy (% shrinkage), and mean FA values. Data are means ± SEM, n = 6 for vehicle (male 3, female 3) and 7 for ZT-1a (male 4, female 3). *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA.